RX − 8564 LC
Page − 35
ETM12E-01
13.6.6. I
2
C bus protocol
In the following sequence descriptions, it is assumed that the CPU is the master and the [ 8564 ] is the slave.
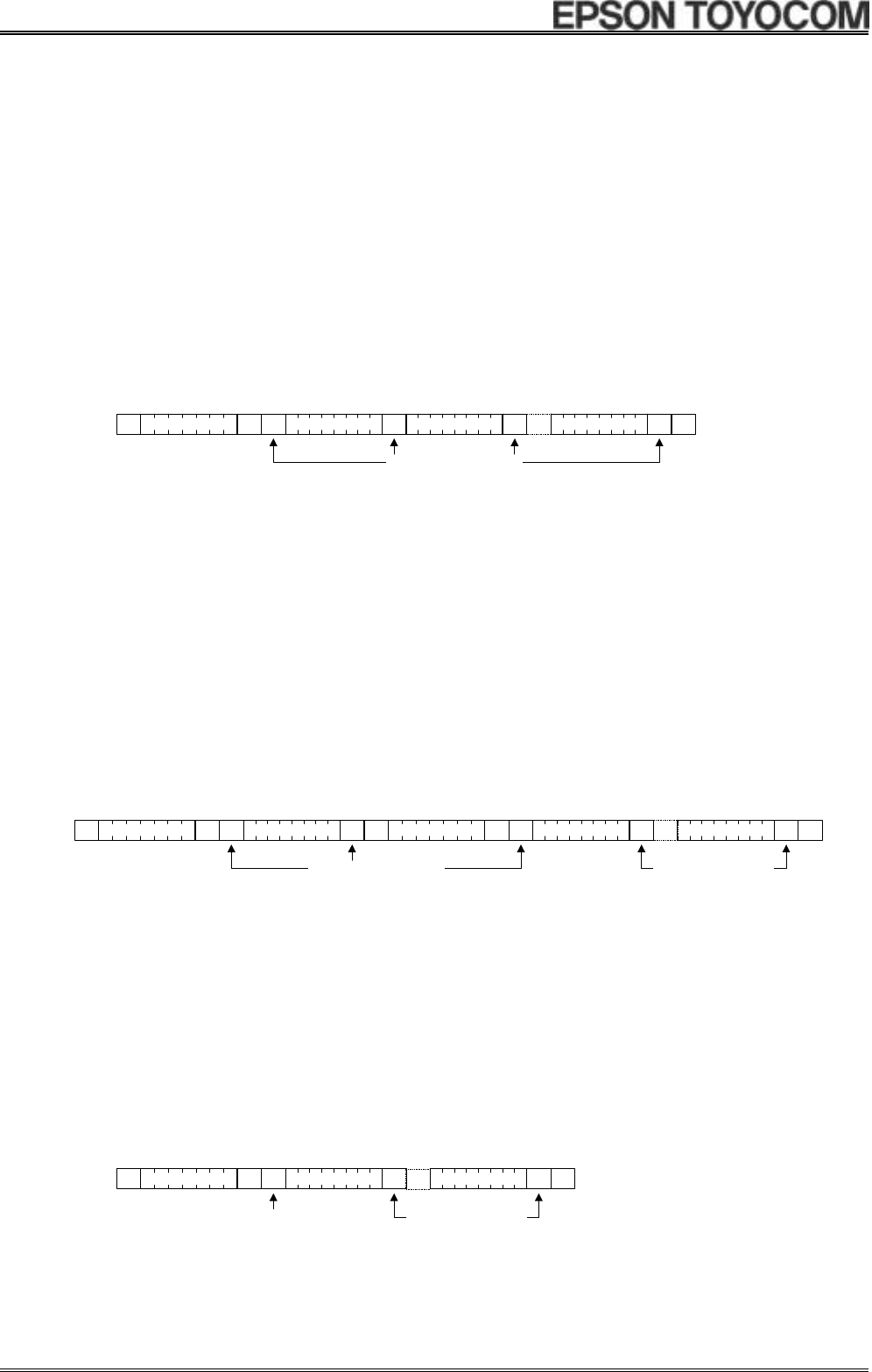
1) Address specification write sequence
Since the [ 8564 ] includes an address auto increment function, once the initial address has been specified, the
[ 8564 ] increments (by one byte) the receive address each time data is transferred.
(1) CPU transfers start condition [S].
(2) CPU transmits the [ 8564 ] 's slave address with the R/W bit set to write mode.
(3) Check for ACK signal from [ 8564 ] .
(4) CPU transmits write address to [ 8564 ] .
(5) Check for ACK signal from [ 8564 ] .
(6) CPU transfers write data to the address specified at (4) above.
(7) Check for ACK signal from [ 8564 ] .
(8) Repeat (6) and (7) if necessary. Addresses are automatically incremented.
(9) CPU transfers stop condition [P].
S
(1)
0
R/W
0
(3)
Address
(4)
0
(5)
0
Data
(8)
P
(9)
ACK signal from
[
8564
]
Data
(6)
0
(7)
(2)
Slave address
2) Address specification read sequence
After using write mode to write the address to be read, set read mode to read the actual data.
(1) CPU transfers start condition [S].
(2) CPU transmits the [ 8564 ] 's slave address with the R/W bit set to write mode.
(3) Check for ACK signal from [ 8564 ] .
(4) CPU transfers address for reading from [ 8564 ] .
(5) Check for ACK signal from [ 8564 ] .
(6) CPU transfers RESTART condition [Sr] (in which case, CPU does not transfer a STOP condition [P]).
(7) CPU transfers [ 8564 ] 's slave address with the R/W bit set to read mode.
(8) Check for ACK signal from [ 8564 ] (from this point on, the CPU is the receiver and the [ 8564 ] is the
transmitter).
(9) Data from address specified at (4) above is output by the [ 8564 ] .
(10) CPU transfers ACK signal to [ 8564 ] .
(11) Repeat (9) and (10) if necessary. Read addresses are automatically incremented.
(12) CPU transfers ACK signal for "1".
(13) CPU transfers stop condition [P].
S
(1)
0
R/W
0
(3)
Address
(4)
Sr
(6)
0
(5)
1
R/W
0
(8)
Data
(9)
0
(10)
Data
(11)
P
(13)
1
(12)
ACK from
[
8564
]
ACK from CPU
(7)
Slave address
(2)
Slave address
3) Read sequence when address is not specified
Once read mode has been initially set, data can be read immediately. In such cases, the address for each read
operation is the previously accessed address + 1.
(1) CPU transfers start condition [S].
(2) CPU transmits the [ 8564 ] 's slave address with the R/W bit set to read mode.
(3) Check for ACK signal from [ 8564 ] (from this point on, the CPU is the receiver and the [ 8564 ] is the
transmitter).
(4) Data is output from the [ 8564 ] to the address following the end of the previously accessed address.
(5) CPU transfers ACK signal to [ 8564 ] .
(6) Repeat (4) and (5) if necessary. Read addresses are automatically incremented in the [ 8564 ] .
(7) CPU transfers ACK signal for "1".
(8) CPU transfers stop condition [P].
S
(1)
1
R/W
0
(3)
Data
(4)
0
(5)
1
(7)
Data
(6)
P
(8)
ACK from CPU
ACK from
[
8564
]
(2)
Slave address


















