EM78P809N
8-Bit Microcontroller
30 •
Product Specification (V1.0) 07.26.2005
(This specification is subject to change without further notice)
8 to 1 Analog switch
ADC
(Successive Approximation)
AD7 (P97)
AD6 (P96)
AD5 (P95)
AD4 (P94)
AD3 (P93)
AD2 (P92)
AD1 (P91)
AD0 (P90)
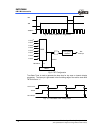
7 - 0 2 1 0
4 to 1
MUX
5 4
Fosc/4
Fosc/16
Fosc/32
5 5 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DATA BUS
IMR1ISFR1ADCRADCRADIC
6 3 7
VDD
VREF
Start to Convert
Power Down
ADCR
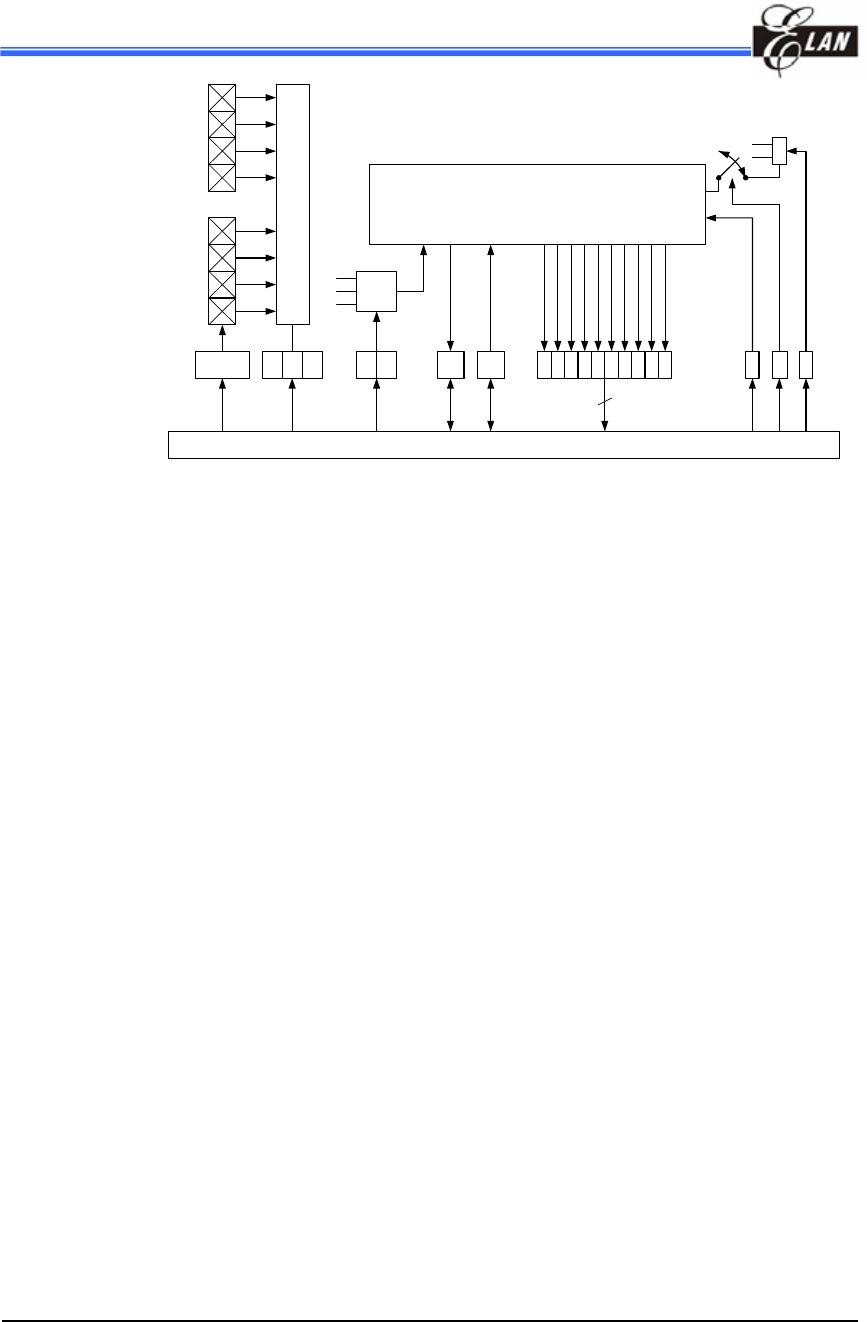
Fig. 6. AD Converter
It is a 10-bit successive approximation type AD converter. The upper side of analog
reference voltage can select either internal VDD or external input pin P97 (VREF) by
setting the ADREF bit in ADCR.
ADC Data Register:
When the A/D conversion is complete, the result is loaded to the ADDH (8 bit) and
ADDL (2 bit). The START/END bit is cleared, and the ADIF is set.
A/D Sampling Time:
The accuracy, linearity, and speed of the successive approximation A/D converter are
dependent on the properties of the ADC. The source impedance and the internal
sampling impedance directly affect the time required to charge the sample holding
capacitor. The application program controls the length of the sample time to meet the
specified accuracy. Generally speaking, the program should wait for 2 μs for each KΩ
of the analog source impedance and at least 2 μs for the low-impedance source. The
maximum recommended impedance for the analog source is 10KΩ at V
DD =5V. After
the analog input channel is selected, this acquisition time must be done before A/D
conversion can be started.
A/D Conversion Time:
ADCK0 and ADCK1 select the conversion time (Tct), in terms of instruction cycles.
This allows the MCU to run at maximum frequency without sacrificing accuracy of A/D
conversion. For the EM78P809N, the conversion time per bit is about 4μs. Table 5
shows the relationship between Tct and the maximum operating frequencies.