Thermal Management Specifications
110 Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-1600 v2/E5-2600 v2 Product Families
Datasheet Volume One of Two
Notes:
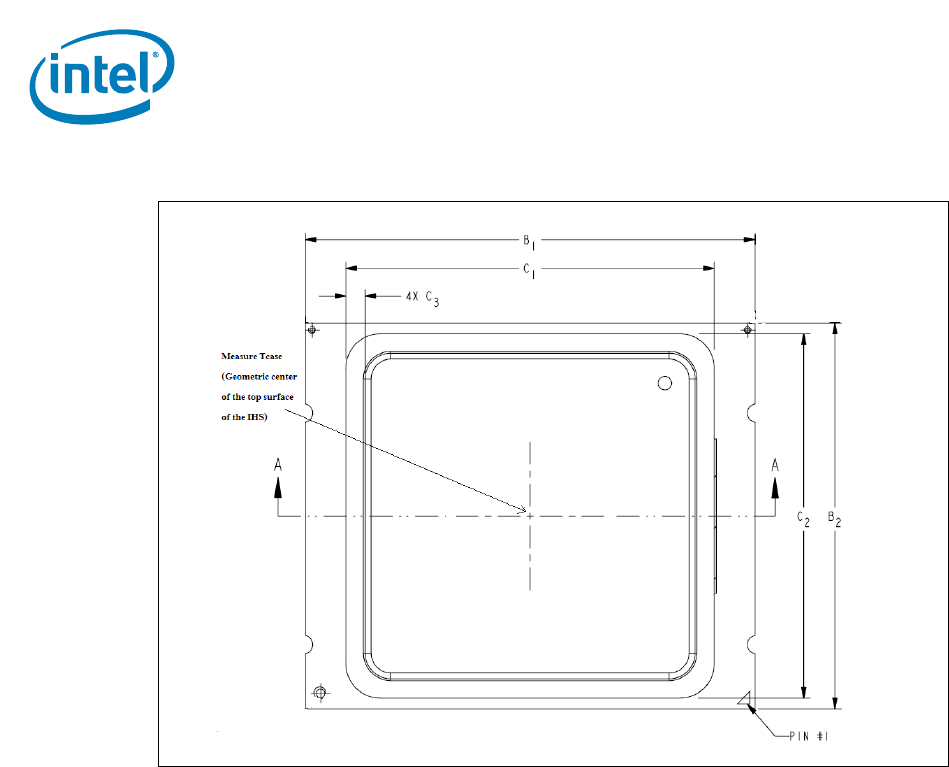
1. Figure is not to scale and is for reference only.
2. This is an example for package size 52.5 x 45 mm.
3. B1: Max = 52.57 mm, Min = 52.43 mm.
4. B2: Max = 45.07 mm, Min = 44.93 mm.
5. C1: Max = 43.1 mm, Min = 42.9 mm.
6. C2: Max = 42.6 mm, Min = 42.4 mm.
7. C3: Max = 2.35 mm, Min = 2.15 mm.
5.2 Processor Core Thermal Features
5.2.1 Processor Temperature
A new feature in the processor is a software readable field in the
TEMPERATURE_TARGET MSR register that contains the minimum temperature at which
the TCC will be activated and PROCHOT_N will be asserted. The TCC activation
temperature is calibrated on a part-by-part basis and normal factory variation may
result in the actual TCC activation temperature being higher than the value listed in the
register. TCC activation temperatures may change based on processor stepping,
frequency or manufacturing efficiencies.
5.2.2 Adaptive Thermal Monitor
The Adaptive Thermal Monitor feature provides an enhanced method for controlling the
processor temperature when the processor silicon reaches its maximum operating
temperature. Adaptive Thermal Monitor uses Thermal Control Circuit (TCC) activation
to reduce processor power via a combination of methods. The first method
(Frequency/SVID control) involves the processor adjusting its operating frequency (via
the core ratio multiplier) and input voltage (via the SVID signals). This combination of
Figure 5-5. Case Temperature (T
CASE
) Measurement Location


















