make up the TMDS data and clock channels. These channels are used to carry video,
audio, and auxiliary data. In addition, HDMI carries a VESA DDC. The DDC is used by
an HDMI Source to determine the capabilities and characteristics of the Sink.
Audio, video, and auxiliary (control/status) data is transmitted across the three TMDS
data channels. The video pixel clock is transmitted on the TMDS clock channel and is
used by the receiver for data recovery on the three data channels. The digital display
data signals driven natively through the PCH are AC coupled and needs level shifting
to convert the AC coupled signals to the HDMI compliant digital signals.
The processor HDMI interface is designed in accordance with the High-Definition
Multimedia Interface with 3D, 4K, Deep Color, and x.v.Color.
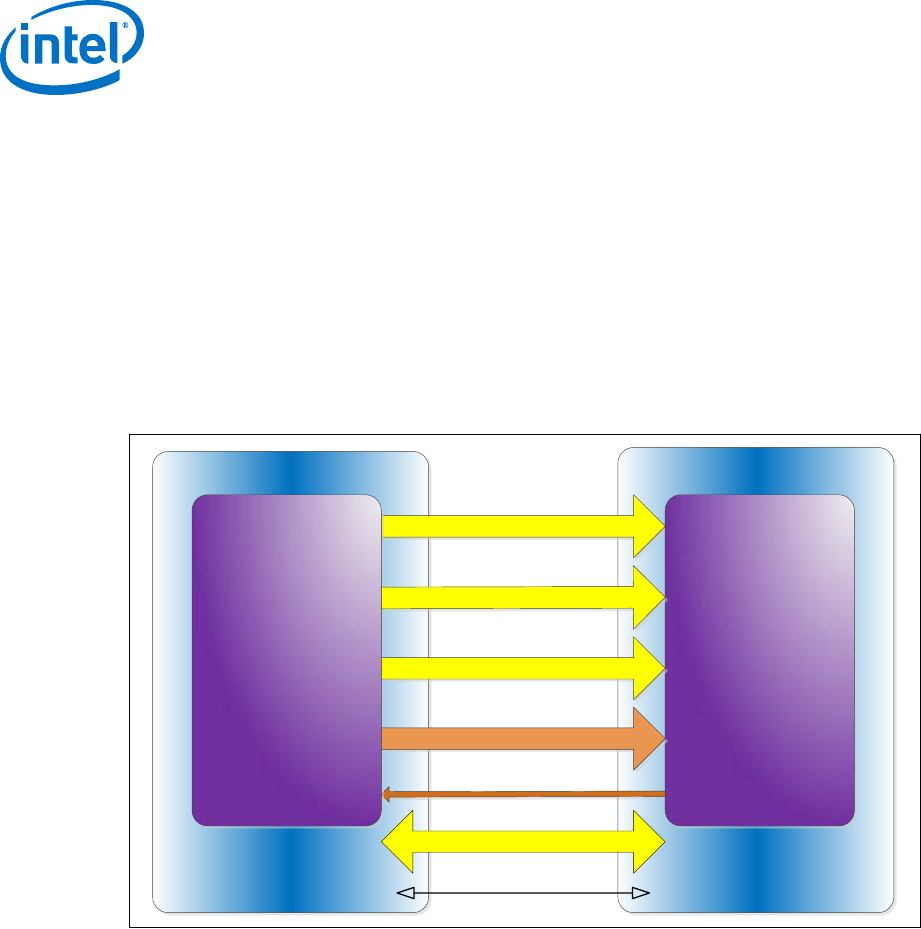
Figure 8. HDMI* Overview
HDMI Source
HDMI Sink
TMDS Data Channel 0
Hot-Plug Detect
HDMI Tx HDMI Rx
TMDS
Data
Channel
1
TMDS Data Channel 2
TMDS Clock Channel
CEC Line (optional)
Display Data Channel (DDC)
Digital Video Interface
The processor Digital Ports can be configured to drive DVI-D. DVI uses TMDS for
transmitting data from the transmitter to the receiver, which is similar to the HDMI
protocol except for the audio and CEC. Refer to the HDMI section for more information
on the signals and data transmission. To drive DVI-I through the back panel the VGA
DDC signals are connected along with the digital data and clock signals from one of
the Digital Ports. When a system has support for a DVI-I port, then either VGA or the
DVI-D through a single DVI-I connector can be driven, but not both simultaneously.
The digital display data signals driven natively through the processor are AC coupled
and need level shifting to convert the AC coupled signals to the HDMI compliant digital
signals.
Processor—Interfaces
Desktop 4th Generation Intel
®
Core
™
Processor Family, Desktop Intel
®
Pentium
®
Processor Family, and Desktop Intel
®
Celeron
®
Processor Family
Datasheet – Volume 1 of 2 December 2013
34 Order No.: 328897-004


















