EDS User Guide 109
13: Modbus
Note: Modbus applies only to EDS4100, as this feature is not supported on EDS8/16/
32PR and EDS8/16PS.
Modbus ASCII/RTU based serial slave devices can be connected via the ethernet through an
existing Modbus TCP/IP network. Any device having access to a given Modbus implementation
will be able to perform full range of operations that the implementation supports. Modbus/TCP
use a reserved TCP port of 502 and include a single byte function code (1=255) preceded by a 6
byte header:
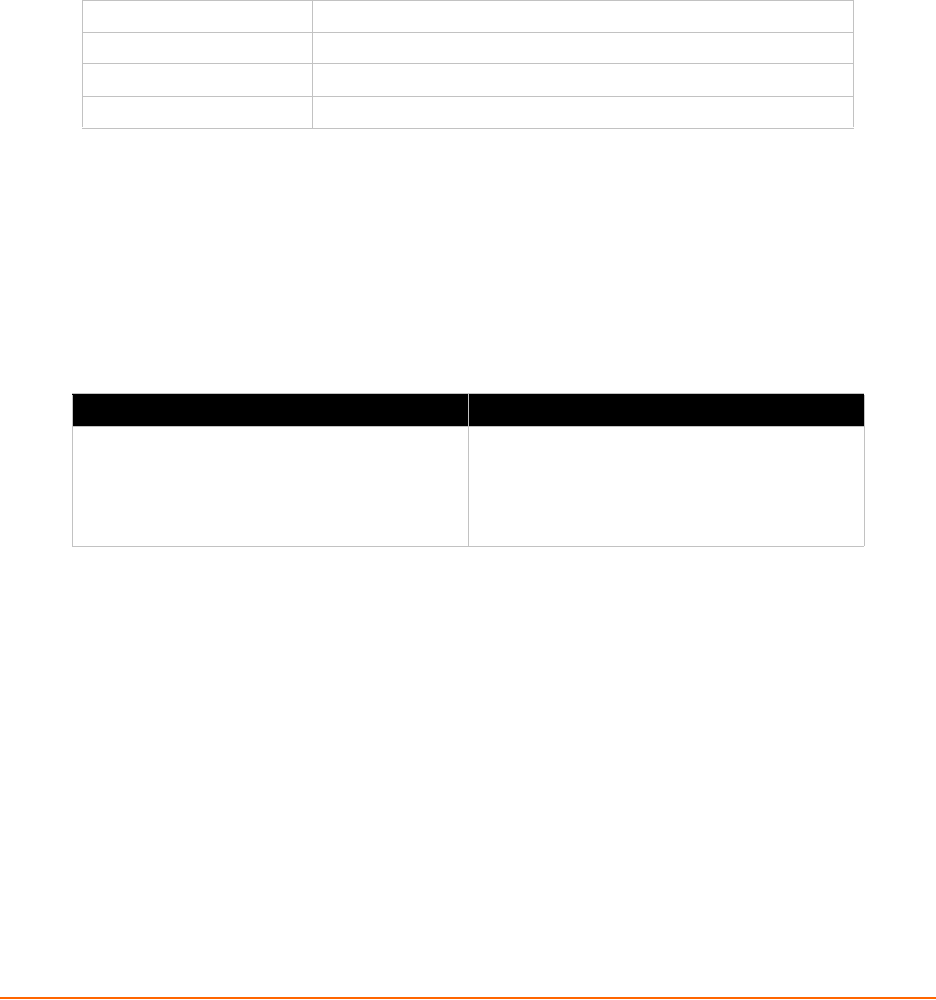
Table 13-1 6 Byte Header of Modbus Application Protocol
Serial Transmission Mode
Evolution products can be set up to communicate on standard Modbus networks using either RTU
or ASCII. Users select the desired mode and serial port communication parameters (baud rate,
parity mode, etc) during the line configuration.
Table 13-2 Modbus Transmission Modes
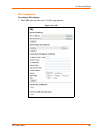
The Modbus web pages allow you to check Modbus status and make configuration changes. This
chapter contains the following sections:
Modbus Statistics
Modbus Configuration
Transaction ID (2 bytes) Identification of request/response transaction - copied by slave
Protocol ID (2 bytes) 0 - Modbus protocol
Length (2 bytes) Number of following bytes includes the unit identifier
Address (1 byte) Identification of remove slave
RTU ASCII
Address: 8 bits (0 to 247 decimal, 0 is used
for broadcast)
Function: 8 bits (1 to 255, 0 is not valid)
Data: N X 8 bits (N=0 to 252 bytes)
CRC Check: 16 bits
Address: 2 CHARS
Function: 2 CHARS
Data: N CHARS (N=0 to 252 CHARS)
LRC Check: 2 CHARS