IP Routing
3-249
3
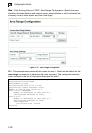
Configuring Network Area Addresses
OSPF protocol broadcast messages (i.e., Link State Advertisements or LSAs) are
restricted by area to limit their impact on network performance. A large network
should be split up into separate OSPF areas to increase network stability, and to
reduce protocol traffic by summarizing routing information into more compact
messages. Each router in an area shares the same view of the network topology,
including area links, route summaries for directly connected areas, and external
links to other areas.
Command Usage
• Use the Network Area Address Configuration page to specify an Area ID and the
corresponding network address range. Each area identifies a logical group of
OSPF routers that actively exchange LSAs to ensure that they share an identical
view of the network topology.
• Each area must be connected to a backbone area. This area passes routing
information between other areas in the autonomous system. The default value
0.0.0.0 is used as the Area ID for the backbone. All routers must be connected to
the backbone, either directly, or through a virtual link if a direct physical connection
is not possible.
• An area initially configured via the Network Area Address Configuration page is set
as a normal area (or transit area) by default. A normal area can send and receive
external Link State Advertisements (LSAs). If necessary, you can use the Area
Configuration page to configure an area as a stubby area that cannot send or
receive external LSAs, or a not-so-stubby area (NSSA) that can import external
route information into its area (page 3-238).
• An area must be assigned a range of subnetwork addresses. This area and the
corresponding address range forms a routing interface, and can be configured to
aggregate LSAs from all of its subnetwork addresses and exchange this
information with other routers in the network (page 3-241).
Command Attributes
• IP Address – Address of the interfaces to add to the area.
• Netmask – Network mask of the address range to add to the area.
• Area ID – Area to which the specified address or range is assigned. An OSPF area
identifies a group of routers that share common routing information. (The area ID
must be in the form of an IP address.)
Note:
This router supports up to 16 total areas (either normal transit areas, stubs, or
NSSAs).