EDS-408A/405A Series User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-21
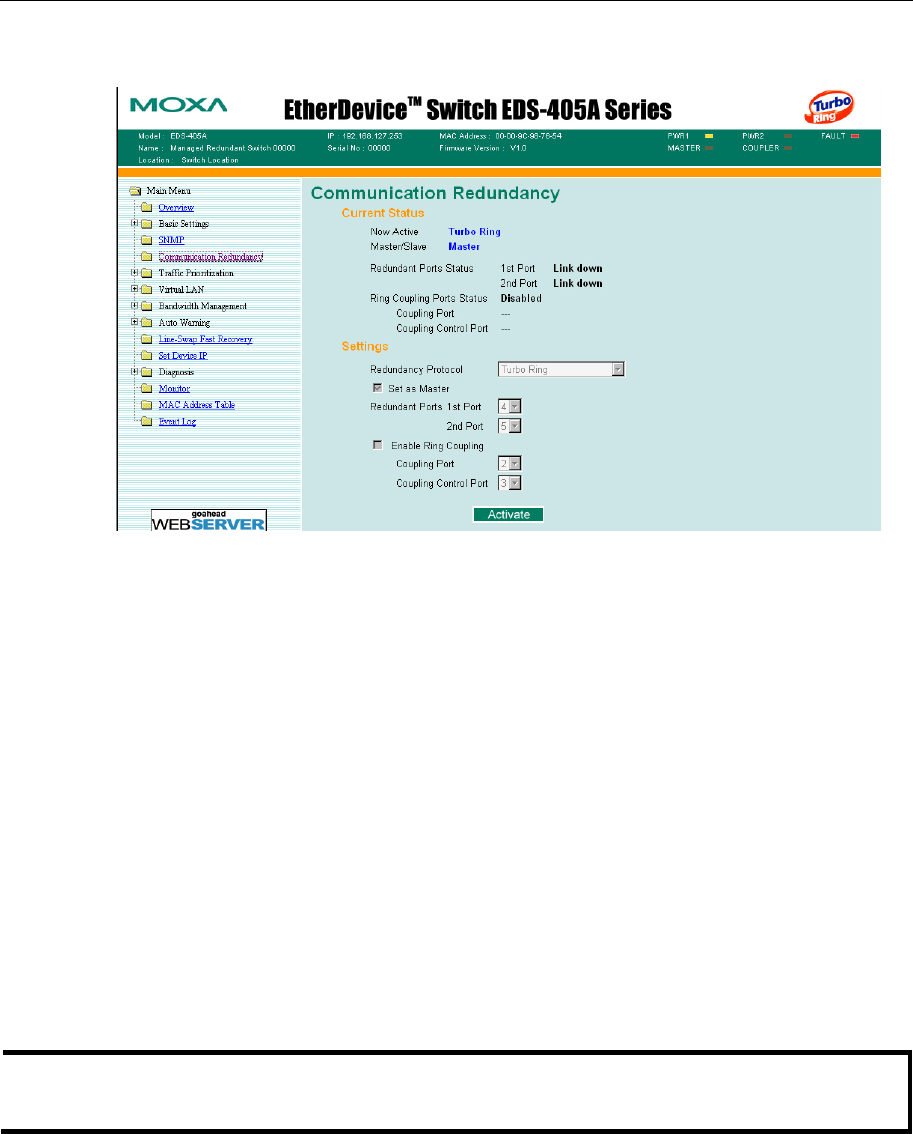
interface to change the status of the DIP Switch. In this case, the Communication Redundancy
settings will be “grayed out,” as shown in the following figure:
The STP/RSTP Concept
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) was designed to help reduce link failures in a network, and provide
protection from loops. Networks that have a complicated architecture are prone to broadcast
storms caused by unintended loops in the network. MOXA EtherDevice Switch’s STP feature is
disabled by default. To be completely effective, you must enable RSTP/STP on every EDS
connected to your network.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) implements the Spanning Tree Algorithm and Protocol
defined by IEEE Std 802.1w-2001. RSTP provides the following benefits:
y The topology of a bridged network will be determined much more quickly compared to STP.
y RSTP is backward compatible with STP, making it relatively easy to deploy. For example:
¾ Defaults to sending 802.1D style BPDUs if packets with this format are received.
¾ STP (802.1D) and RSTP (802.1w) can operate on different ports of the same EDS. This
feature is particularly helpful with EDS ports connect to older equipment, such as legacy
switches.
You get essentially the same functionality as STP with RSTP. To see how the two systems differ,
see the Differences between RSTP and STP section in this chapter.
NOTE
The STP protocol is part of the IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition bridge specification. The
following explanation uses bridge instead of switch.
What is STP?
STP (802.1D) is a bridge-based system that is used to implement parallel paths for network traffic.
STP uses a loop-detection process to: