EDS-408A/405A Series User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-31
2. Because the 802.1p priority levels are fixed to the traffic queues, the packet will be placed in
the appropriate priority queue, ready for transmission through the appropriate egress port.
When the packet reaches the head of its queue and is about to be transmitted, the device
determines whether or not the egress port is tagged for that VLAN. If it is, then the new
802.1p tag is used in the extended 802.1D header.
The EDS will check a packet received at the ingress port for IEEE 802.1D traffic classification,
and then prioritize it based upon the IEEE 802.1p value (service levels) in that tag. It is this 802.1p
value that determines which traffic queue the packet is mapped to.
Traffic Queues
The EDS hardware has multiple traffic queues that allow packet prioritization to occur. Higher
priority traffic can pass through the EDS without being delayed by lower priority traffic. As each
packet arrives in the EDS, it passes through any ingress processing (which includes classification,
marking/re-marking), and is then sorted into the appropriate queue. The switch then forwards
packets from each queue.
EDS supports two different queuing mechanisms:
y Weight Fair: This method services all the traffic queues, giving priority to the higher priority
queues. Under most circumstances, this method gives high priority precedence over
low-priority, but in the event that high-priority traffic exceeds the link capacity, lower priority
traffic is not blocked.
y Strict: This method services high traffic queues first; low priority queues are delayed until no
more high priority data needs to be sent. This method always gives precedence to high priority
over low-priority.
Configuring Traffic Prioritization
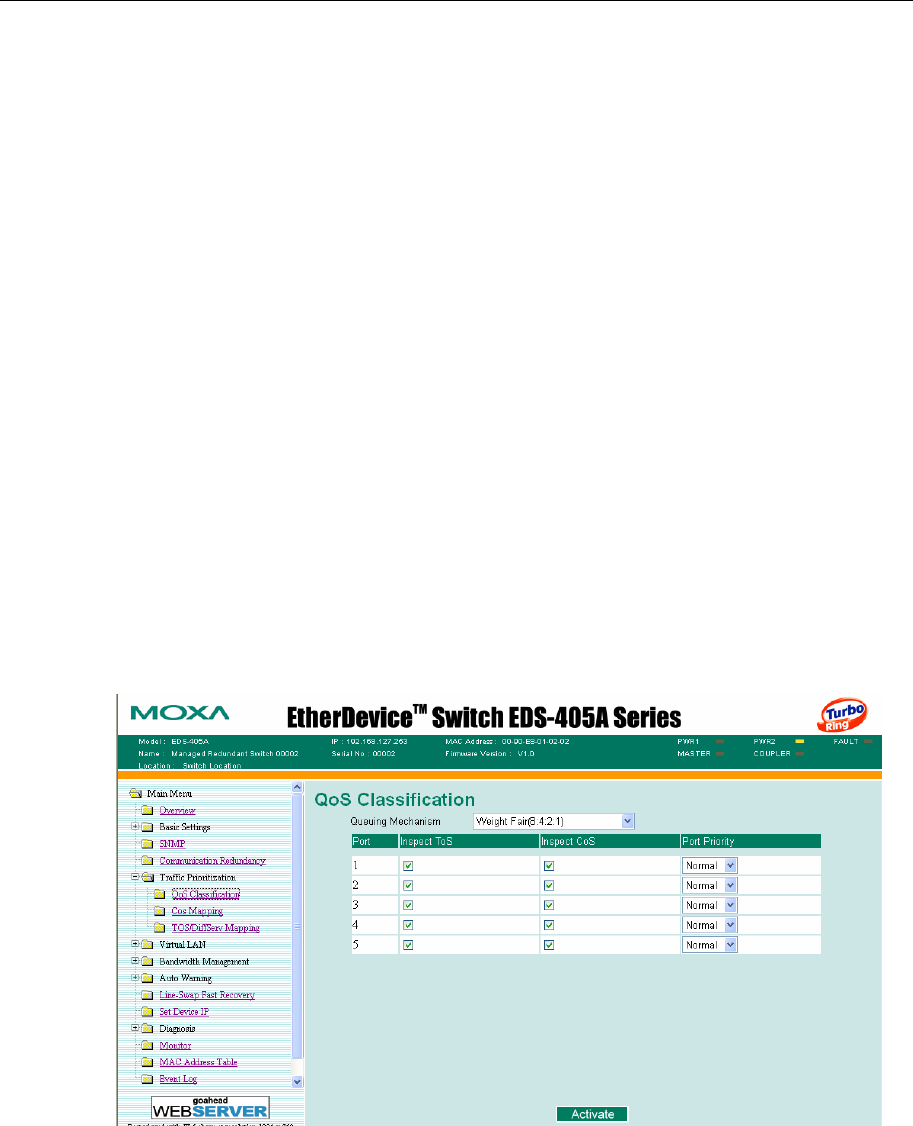
QoS Classification
MOXA EtherDevice Switch supports inspection of layer 3 TOS and/or layer 2 QoS tag
information to determine how to classify traffic packets. (NOTE: The user interface for EDS-408A
shows 8 ports.)


















