EDS-408A/405A Series User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-23
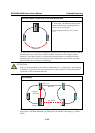
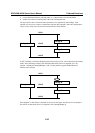
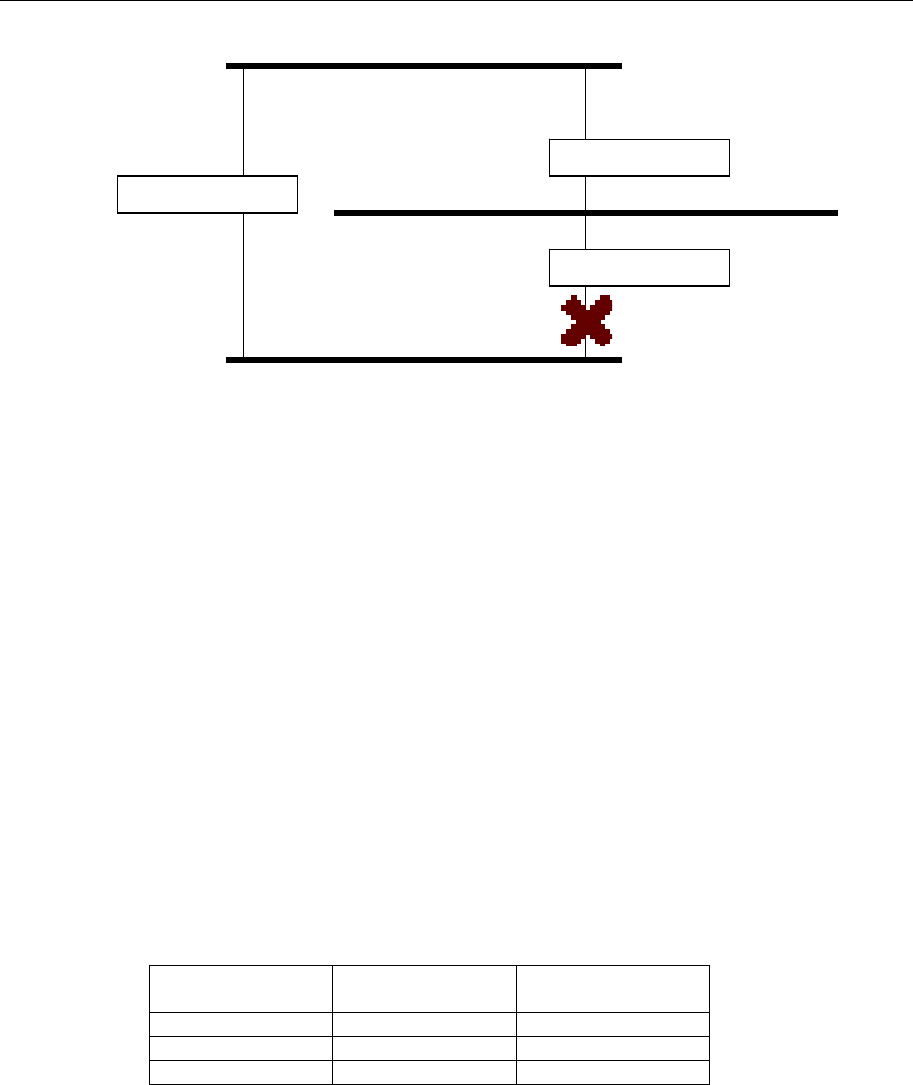
STP determines which path between each bridged segment is most efficient, and then assigns a
specific reference point on the network. When the most efficient path has been identified, the other
paths are blocked. In the previous 3 figures, STP first determined that the path through Bridge C
was the most efficient, and as a result, blocked the path through Bridge B. After the failure of
Bridge C, STP re-evaluated the situation and opened the path through Bridge B.
How STP Works
When enabled, STP determines the most appropriate path for traffic through a network. The way it
does this is outlined in the following sections.
STP Requirements
Before STP can configure the network, the system must satisfy the following requirements:
y Communication between all the bridges. This communication is carried out using Bridge
Protocol Data Units (BPDUs), which are transmitted in packets with a known multicast
address.
y Each bridge must have a Bridge Identifier that specifies which bridge acts as the central
reference point, or Root Bridge, for the STP system—bridges with a lower Bridge Identifier
are more likely to be designated as the Root Bridge. The Bridge Identifier is calculated using
the MAC address of the bridge and a priority defined for the bridge. The default priority of
EDS is 32768.
y Each port has a cost that specifies the efficiency of each link. The efficieny cost is usually
determined by the bandwidth of the link, with less efficient links assigned a higher cost. The
following table shows the default port costs for a switch:
Port Speed Path Cost 802.1D,
1998 Edition
Path Cost
802.1w-2001
10 Mbps 100 2,000,000
100 Mbps 19 200,000
1000 Mbps 4 20,000
STP Calculation
The first step of the STP process is to perform calculations. During this stage, each bridge on the
network transmits BPDUs. The following items will be calculated:
y The bridge that should be the Root Bridge. The Root Bridge is the central reference point
from which the network is configured.
y The Root Path Costs for each bridge. This is the cost of the paths from each bridge to the Root
Bridge.
Brid
g
e B
Brid
g
e C
LAN 1
LAN 2
LAN 3
Brid
g
e A