COMSPHERE 3600 Series Data Service Units
4-14 March 1999 3610-A2-GB41-60
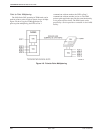
FEP Port Sharing
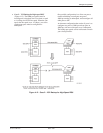
FEP port sharing is a method of connecting a front-end
processor (FEP) to multiple control DSUs/modems to
broadcast the same message over different circuits, yet
receive individual responses. A typical example can be
found in the retail banking environment (Figure 4-10),
where two high-speed applications (Channels A and B in
the figure) service a branch of a retail bank, and the lower
speed automated teller machine (ATM) application
(Channel C in the figure) services an ATM at the retail
branch as well as several remote ATMs. The ATM
application is extended by a FEP port-sharing group
(Ports 3 and 4) at the control DSU and by a dedicated
multipoint circuit.
NOTE
When FEP port sharing is
enabled, the corresponding port
must operate in switched-carrier
mode. V.13 Signaling may be
used.
Set the tributary DSU’s port
RTS Cntrl configuration option to
DTE and its TxCarrSel
configuration option to Cntrl.
Set
the control DSU’s port
RxCarrSel
configuration option to Cntrl.In
addition, at the control DSU,
FEP port sharing can be
combined with digital sharing at
one or more tributary DSUs. In
this case, V.13 Signaling
cannot
be used. Instead, the control DSU
must have its RxCarrSel
configuration option set to Mark.
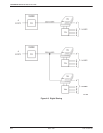
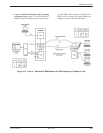
FEP port sharing is accomplished with adjacent pairs
of ports on the TDM or MCMP circuit card. Up to three
separate groups can be selected, Ports 1 and 2, Ports 3 and
4, and/or Ports 5 and 6. FEP transmit data, receive data,
and controls pass through the lower-numbered port of a
FEP port-sharing group to be broadcast onto the aggregate
data path and to the higher-numbered port. For example,
data transmitted from the FEP on Port 3 is sent to the
DSU connected to Port 4 and to Channel C of the TDM
(Figure 4-10). Data received from Channel C or Port 4 is
sent to the FEP on Port 3.
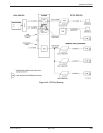
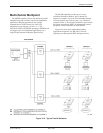
FEP port sharing is also used to back up an MCMP
circuit with a set of point-to-point TDM circuits. The
MCMP Backup section describes this in detail.