COMSPHERE 3600 Series Data Service Units
4-38 March 1999 3610-A2-GB41-60
Diagnostic Considerations
The digital bridge joins the aggregate data stream,
including data, framing bits, and diagnostics. The
diagnostic communication with tributary DSUs and
DBMs is transparent to the digital bridge. Commands for
a tributary DSU or DBM can be addressed via the control
DSU, even when in backup. The central-site DBM-Vs,
DBM-Ss, and DBM-Ds should be configured for
disruptive diagnostics.
For a central-site bridge configuration, nondisruptive,
mixed, and disruptive diagnostic types (3600e, Br56) are
supported. Rate adaption is not supported. Therefore, the
DSU port speed must equal the DSU rate and the bridge
rate must equal the DBM rate. Also, the Multipoint
Symmetrical (M-PtSymPrt) configuration option must be
disabled.
NOTE
References to DBM in this guide
also apply to a DBM-V, DBM-S,
or DBM-D.
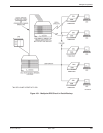
Multipoint Backup
The digital bridge capability of the TDM or MCMP
option allows multipoint DDS circuits to have backup
capability. At the central site, in addition to a TDM or
MCMP, a DBM-V or DBM-S is required for each
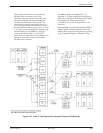
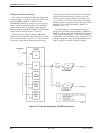
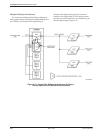
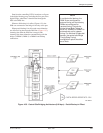
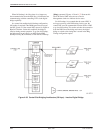
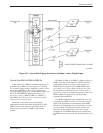
tributary DSU to be backed up (Figure 4-31).
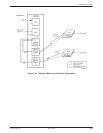
Multipoint backup can provide dedicated dial backup
on multipoint DDS circuits. Figure 4-28 shows the
multipoint tributary DSUs as 3610 DSUs/DBMs, but
tributaries can also be 3611 DSUs/DBMs. One dial
backup call is required per failed drop.
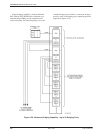
Partial backup on multipoint DDS circuits is possible
when not all drops are out-of-service, as long as the speed
of the DDS line and the dial backup modules are matched
and the digital bridge rate is set to =DSU. In partial
backup, the tributaries not affected by the failure continue
to communicate with the control DSU through the DDS
facility, and each tributary affected by the failure
communicates with the control DSU through a backup
connection.
Full backup to each tributary on multipoint circuits is
necessary when the speed of the DDS line and the dial
backup modules cannot be matched or when the DDS
facility (backbone) goes out-of-service. In full backup, the
DDS facility is dropped and each tributary DSU
communicates with the control DSU through a backup
connection.
A partial backup application is shown in Figure 4-31.
Each pair of communicating DBMs includes a
central-site, carrier-mounted dial backup module
(DBM-V, DBM-S, or DBM-D) and a remote-site
childboard DBM. The DBM-V, DBM-S, or DBM-D is a
dial backup module that fits into a COMSPHERE 3000
Series Carrier. The DBM can be addressed by an NMS, an
async terminal, or the SDCP, can accept and forward
diagnostic messages, and can carry out commands
essential to multipoint dial backup operation.
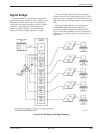
The digital bridge and DBM-Vs, DBM-Ss, or DBM-Ds
are dedicated to a single DSU. Digital bridging of the
DTE input/output signals on Port 1 of the control DSU is
performed by the TDM or MCMP circuit card. The circuit
card broadcasts Port 1 DTE data to the central-site
DBM-Vs, DBM-Ss, or DBM-Ds and accepts data from
them when they are in dial backup.
Multipoint dial backup requires the following hardware
when there are five or fewer drops:
• One Model 3611 DSU configured as a control.
• One TDM or MCMP circuit card configured as a
digital bridge.
• One DBM-V, DBM-S, or DBM-D per drop at the
central site. (The modules do not need to be
adjacent to the TDM or MCMP circuit card or even
in the same carrier as the TDM or MCMP.) A
digital bridge interface or crossover cable between
the digital bridge ports and the DBM-Vs, DBM-Ss,
or DBM-Ds is required.
• One DBM in each tributary DSU.
One TDM or MCMP circuit card operating in Bridge
mode can provide dial backup for up to five tributary
DSUs. Bridges can be extended to provide dial backup for
up to 20 tributary DSUs (see the Digital Bridge section of
this chapter and Appendix D, Configuration Scenarios,
for more information).