3. DSL Card Configuration
8000-A2-GB26-50 April 2001
3-21
6. For all SNs except the DSL Router, enter
enabled
at the
Enabled/Disabled:
prompt in the IP Scoping field. (Default = enabled.)
You can also enable IP Scoping on port cards with a DSL Router SN except
under certain conditions. See
Exception When Using a DSL Router
.
7. If desired, enter an ISP domain name at the
Domain Name:
prompt
(30 characters maximum).
Example: If entering a VNID for XYZ Company, enter
XYZ
as the Domain
Name.
8. Enter
yes
at the
yes/no:
prompt to save your changes.
Changing the Existing VNIDs or VNID Attributes
If a new VNID is activated on the DSL port, relocate all clients to the new VNID
(with user’s approval). Otherwise, delete all clients associated with the old VNID.
Also, if IP Scoping is disabled for the new VNID but was enabled for the old VNID,
delete all dynamic client entries (along with their associated ARP and MAC
entries).
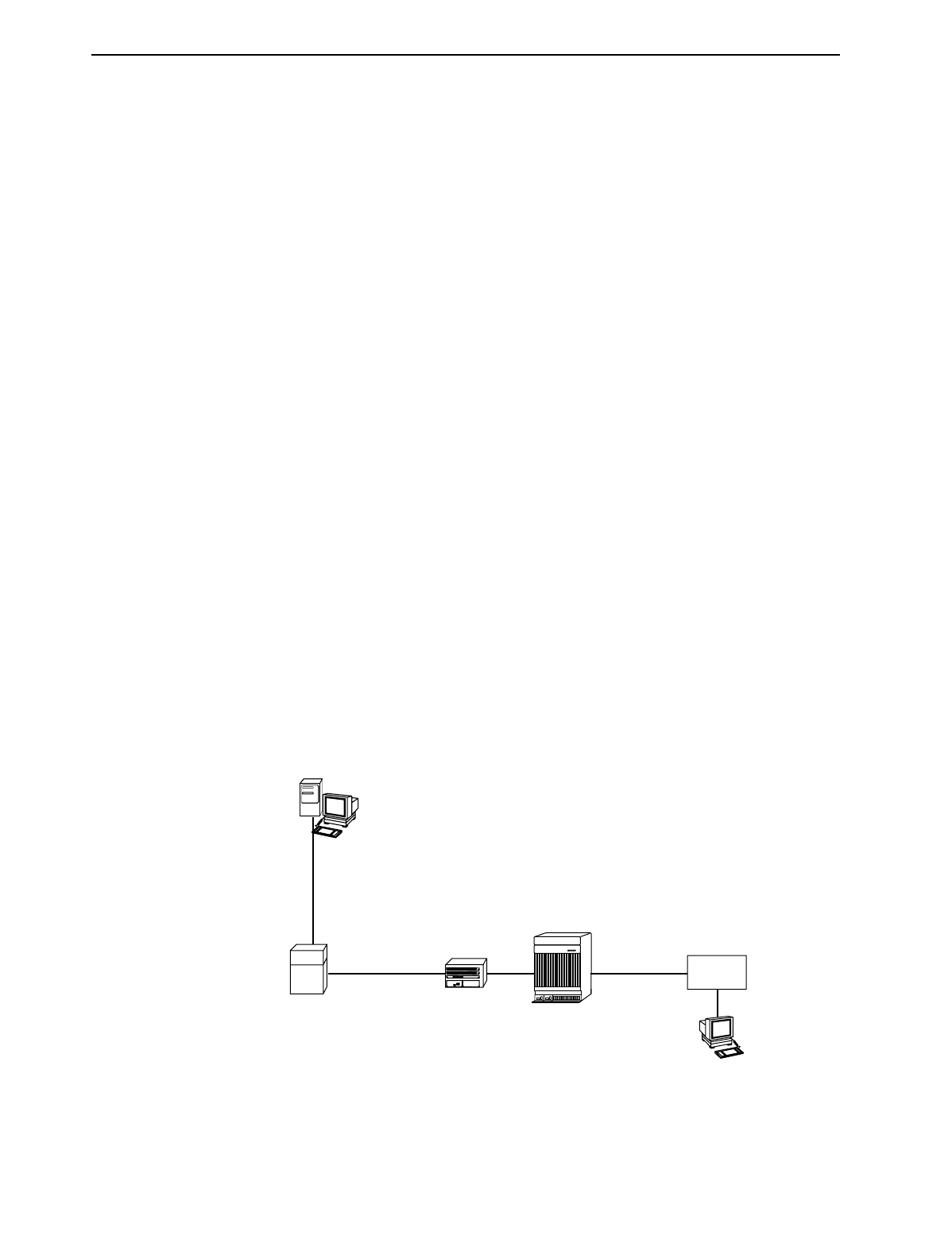
Exception When Using a DSL Router
This section presents an example of an exception when IP Scoping must be
disabled when using a DSL Router. IP Scoping on the port card must be disabled
if the DHCP relay capability on the DSL Router is enabled, and the IP addressing
scheme allows the core device at the access provider’s location to ARP directly for
the client behind the DSL Router. In the figure below, the Cisco Router ARPs
directly for the client PC. Therefore, IP Scoping must be disabled on the port card
for proper data communication.
00-16694-01
DHCP Server
195.190.118.121
Scope 206.135.206.10-206.135.206.20
255.255.255.0
Router 206.135.206.253
Cisco Router
BVI 49
206.135.206.1
255.255.255.0
IPC
8820
VNID 49
MUX=ON,
Filter=OFF, Scoping=OFF
NHR
206.135.206.1
d0 Proxy ARP
Unnumbered
e0 Proxy ARP
206.135.206.253
255.255.255.0
PC
DSL
Router
O
I
206.135.206.10
255.255.255.0


















