IP Addressing
5-2
8700-A2-GB20-00
April 2000
Review the following information in preparation for selecting an IP addressing
scheme.
H Any legal host address is allowed for a given subnet. The address choice
within the subnet is arbitrary.
H A single route to a subnet is all that is needed to reach every device on a
subnet. The unit’s routing table supports a maximum of 20 routes.
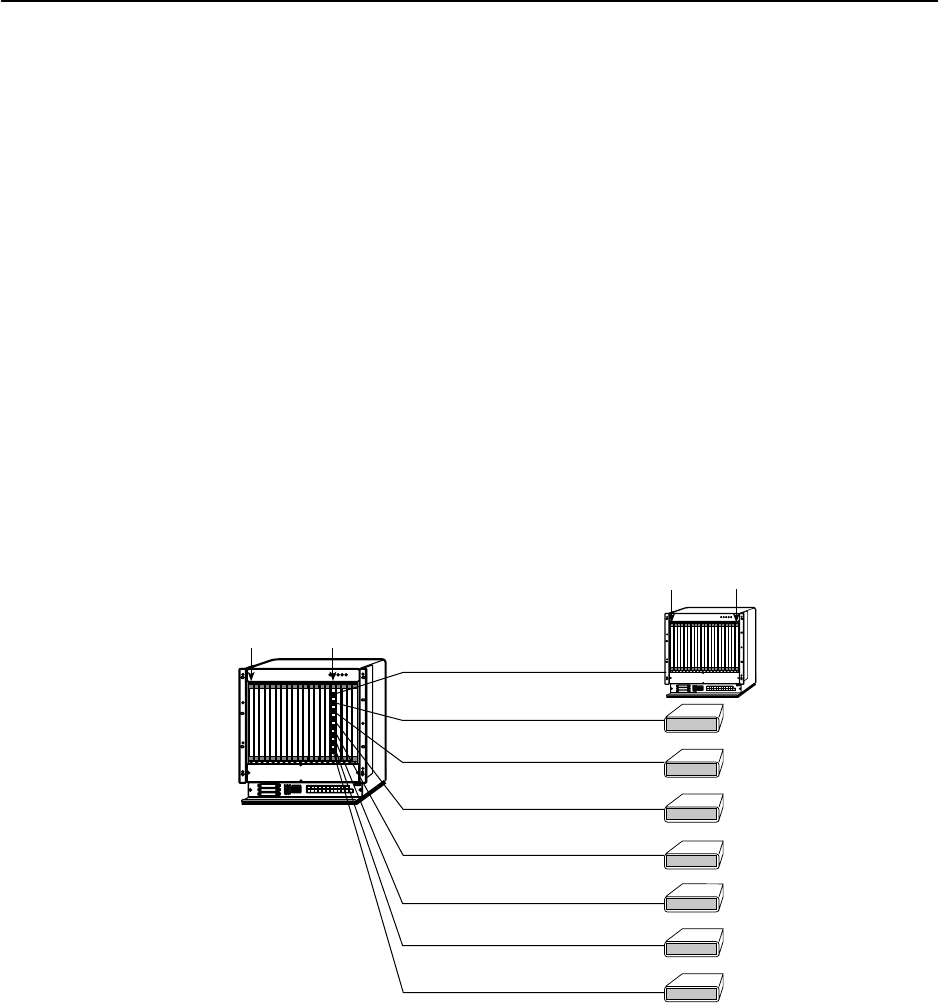
IP Addressing Example
The following diagram shows IP addressing in a typical network. Note that:
H The Peer IP Address refers to the IP address of the unit configured as an
NTU.
H The Peer IP Address is assigned by the LTU.
99-16617
DSLAM
DSLAM
79xx
79xx
79xx
MCC Base
Address = 126.35.50.1
MCC Base Subnet
Mask = 255.255.255.0
Port 1
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.32
MCC
LTU
87xx
Port 2
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.33
Port 3
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.34
Port 4
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.35
NTU
MCC
MCC Backplane
Address = 126.35.1.1
MCC Backplane
Mask = 255.255.255.0
LTU Backplane
Address = 126.35.1.16
NTU Backplane
Address = 126.35.50.17
79xx
79xx
79xx
Port 5
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.36
Port 6
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.37
Port 7
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.38
Port 8
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.39
79xx
Peer IP Address Assignments