Software Configuration Overview 39
Model 3124 User Manual 3 • Configuration
Fault Management
Fault management is conceptually partitioned into two levels: the system top level, and interface-specific level.
Both levels are alarm-level configurable and can be Major and Minor. All the alarms are mask-able.
Fault management provides the alarm output through hardware output interface (on the system front panel)
and visible indicator (LED). The alarm/status indications are automatically generated as a result of certain
events/conditions. The Model 3124 supports query of all current alarm status. It is also able to keep 256
records of historical alarms and events respectively.
The Model 3124 provides the ability to group alarms in a hierarchical alarm presentation scheme. Alarms of
the same rank can exist at the same time. A lower-ranking alarm will be demoted if a higher-ranking alarm is
raised for the same object. For example, if a far-end LOS is raised on a circuit and then a far-end LPR is raised
on the circuit, the LPR alarm stands and the LOS closes. The alarm hierarchy used in the Model 3124 system
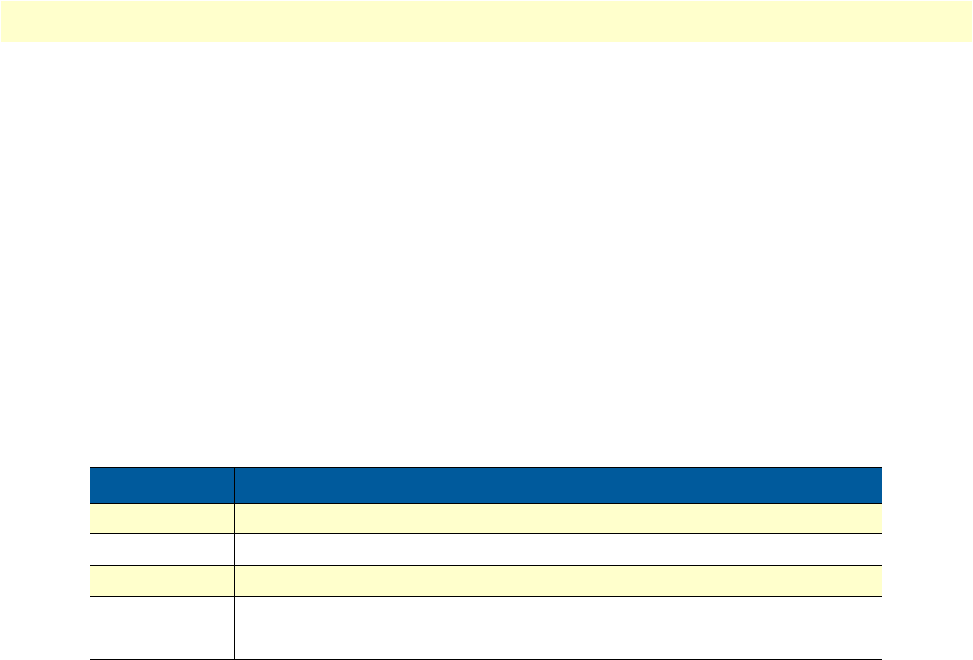
is shown in the following table:
Note
LOM, LCD, and NCD are not included in the alarm hierarchy;
they’re treated independently.
Note
The PM counters LPR, LOS, and LOF follow the alarm hierarchy
rule. When these alarms exist at the same time, only the PM counter
of a higher-ranking alarm will count (the PM counters of other lower-
ranking alarms will not).
System Alarms
The Model 3124 provides the following System alarms:
• Fan Failure Alarm
• Above Temperature
• Below Temperature
• Self-test Fail
• DSP Fail - you can see which DSP chip is fail from the user interface (Web GUI, CLI, etc.). There is a
number 1 ~ 4 in the alarm message/description corresponding to the DSP chip 1 ~ chip 4
Table 15. Model 3124 Alarm Hierarchy
Priority Alarm Type
Highest all activation failures (ADSL_COMMF_FE or ADSL_NOPEER_FE)
—
far-end LPR
—
near-end LOS or far-end LOS
Lowest near-end LOF or far-end LOF (near-end and far-end are independent;
for example, FE-LOS does not restrain NE-LOF)