Chapter 6 Advanced Topics 63
63
Pin #
Assignment
Pin #
Assignment
1
IN 1
14
IN 2
2
IN 3
15
IN 4
3
IN 5
16
IN 6
4
IN 7
17
IN 8
5
GND
18
GND
6
EN/CLK
19
Reserved
7
(future use)
20
GND
8
GND
21
OUT 2
9
OUT 1
22
OUT 4
10
OUT 3
23
OUT 6
11
OUT 5
24
OUT 8
12
OUT 7
25
GND
13
Reserved
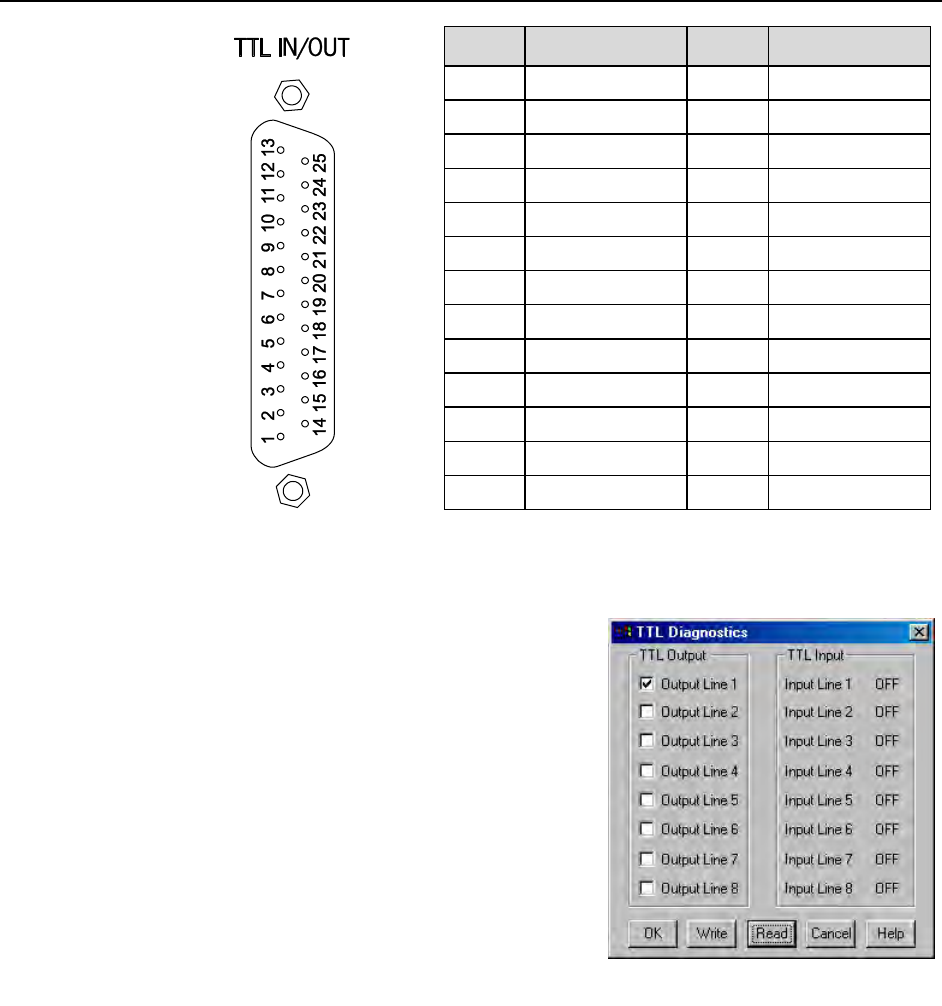
Figure 29. TTL In/Out
Connector
Table 5. TTL In/Out Connector Pinout
TTL Diagnostics Screen
Note that WinView/32 and WinSpec/32 provide a
TTL Diagnostics screen (located in WinView/32
under Hardware Setup|Diagnostics) that can
be used to test and analyze the TTL In/Out lines.
Hardware Interface
A cable will be needed to connect the TTL In/Out
connector to the experiment. The design will vary
widely according to each user’s needs, but a
standard 25-pin female type D-subminiature
connector will be needed to mate with the TTL
In/Out connector on the back of the ST-133. The
hardware at the other end of the cable will depend
entirely on the user’s requirements. If the
individual connections are made using coaxial
cable for maximum noise immunity
(recommended), the center conductor of the coax should connect to the proper signal pin
and the cable shield should connect to the nearest available ground (grounds are
conveniently provided at pins 5, 8, 18 and 20). Connector hardware and cables of many
different types are widely available and can often be obtained locally, such as at a nearby
Radio Shack
®
store. A list of possibly useful items follows. Note that, although the items
listed may be appropriate in many situations, they might not meet your specific needs.
25-pin female type D-subminiature solder type connector (Radio Shack
®
part number
276-1548B).
RG/58U coaxial cable.
Figure 30. TTL Diagnostics dialog