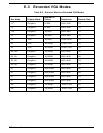
D.2.1 Extended Memory
Extended Memory is defined as internal system RAM above 1024 KB.
MS-DOS or your applications (that support Extended Memory) can access
Extended Memory if your system is configured with an Extended Memory
driver (XMS). Extended Memory drivers manage the Extended Memory
ensuring that two programs do not use the same part of memory. The
enhanced mode of MS Windows uses Extended Memory to multitask
applications.
MS-DOS includes the HIMEM.SYS Extended Memory driver. HIMEM.SYS is
defined in your CONFIG.SYS file where it is automatically loaded each time
you boot the system. HIMEM.SYS also enables MS-DOS programs to use an
extra 64-KB region located just above the 1-MB mark for storage of code
and data. This area is known as high memory area (HMA).
n
Note: MS-DOS can also be loaded in HMA to free up conventional memory. Re-
fer to your MS-DOS User’s Manual for instructions.
n
Note: Some application programs that run in 386 enhanced mode (such as
Windows) require special Extended Memory managers. Use the Extended
Memory manager provided with your application, if available. Otherwise,
use HIMEM.SYS, the MS-DOS version furnished with the computer.
You can define part of Extended Memory as one or more RAM disks using
the RAMDRIVE.SYS device driver. Details are provided in the paragraph
D.2.2.
D.2.2 Expanded Memory
Expanded Memory conforms to the Expanded Memory Specification (EMS)
developed by Lotus/Intel/Microsoft (LIM) known as LIM-EMS. Your
computer supports EMS version 4.0.
Expanded Memory is accessed by allocating an area (usually 64 KB) of
system memory between 640 KB and 1 MB (and between 256 KB and 640
KB when the
/O option is used) as a “window.” Pages or segments of data
are passed to and from Expanded Memory through this window, which is
called the page frame. The page frame is divided into at least four physical
pages of 16 KB each.
The total amount of internal memory above 640 KB can be assigned to
either Extended Memory (XMS) or Expanded Memory (EMS), depending on
your requirements and which driver is installed.
n
Note: MS Windows can use both XMS and EMS in 386 Enhanced mode when
properly configured. Refer to your Windows User’s Guide for details and in-
structions.
D-2 Configuring Memory