Multicast address: An identifier for a set of interfaces (typically belonging to different nodes),
similar to an IPv4 multicast address. A packet sent to a multicast address is delivered to all
interfaces identified by that address. There are no broadcast addresses in IPv6. Their
function is superseded by multicast addresses.
Anycast address: An identifier for a set of interfaces (typically belonging to different nodes).
A packet sent to an anycast address is delivered to one of the interfaces identified by that
address (the nearest one, according to the routing protocols’ measure of distance).
The type of an IPv6 address is designated by the first several bits called format prefix. The
following table lists the mappings between address types and format prefixes.
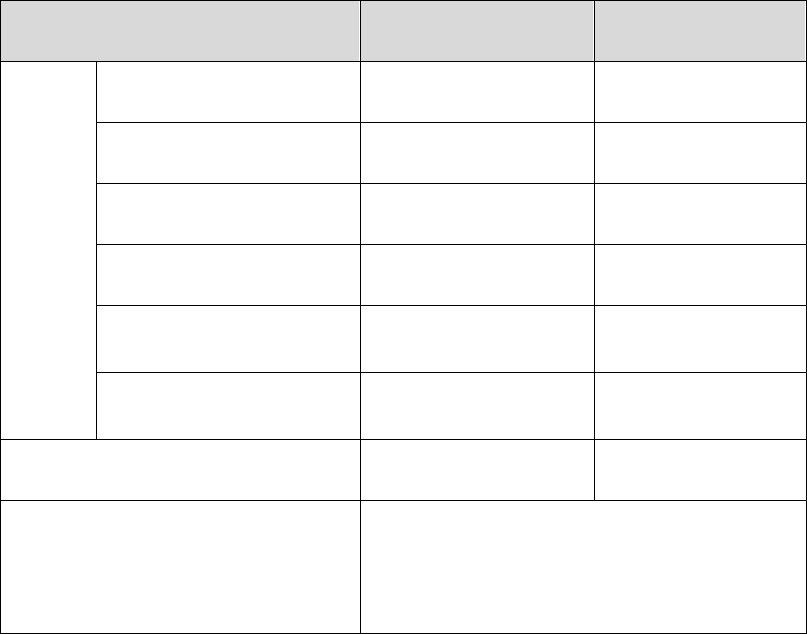
Type Format Prefix (binary) IPv6 Prefix ID
Unicast
address
Unassigned address 00…0 (128 bits) ::/128
Loopback address 00…1 (128 bits) ::1/128
Link-local address 1111111010 FE80::/10
Site-local address 1111111011 FEC0::/10
Global unicast address
(currently assigned)
001 2xxx::/4 or 3xxx::/4
Reserved type
(to be assigned in future)
Other formats
Multicast address 11111111 FF00::/8
Anycast address
Anycast addresses are taken from unicast
address space and are not syntactically
distinguishable from unicast addresses.
Table 4-1 Mappings between address types and format prefixes
3. IPv6 Unicast Address:
IPv6 unicast address is an identifier for a single interface. It consists of a subnet prefix and an
interface ID.
Subnet Prefix: This section is allocated by the IANA (The Internet Assigned Numbers
Authority), the ISP (Internet Service Provider) or the organizations.
Interface ID: An interface ID is used to identify interfaces on a link. The interface ID must be
unique to the link.
There are several ways to form interface IDs. The IPv6 addresses with format prefixes 001
through 111, except for multicast addresses (1111 1111), are all required to have 64-bit
interface IDs in EUI-64 format.
21


















