For the member ports in an aggregation group, their basic configuration must be the same. The
basic configuration includes STP, QoS, GVRP, VLAN, port attributes, MAC Address Learning
mode and other associated settings. More details are explained below:
If the ports, which are enabled for the GVRP, 802.1Q VLAN, Voice VLAN, STP, QoS, DHCP
Snooping and Port Configuration (Speed and Flow Control), are in a LAG, their
configurations should be the same.
The ports, which are enabled for the half-duplex, Port Security, Port Mirror, MAC Address
Filtering, Static MAC Address Binding and 802.1X Authentication, cannot be added to the
LAG.
It’s not suggested to add the ports with ARP Inspection and DoS Defend enabled to the
LAG.
If the LAG is needed, you are suggested to configure the LAG function here before configuring the
other functions for the member ports.
Tips:
1. Calculate the bandwidth for a LAG: If a LAG consists of the four ports in the speed of
1000Mbps Full Duplex, the whole bandwidth of the LAG is up to 8000Mbps (2000Mbps * 4)
because the bandwidth of each member port is 2000Mbps counting the up-linked speed of
1000Mbps and the down-linked speed of 1000Mbps.
2. The traffic load of the LAG will be balanced among the ports according to the Aggregate
Arithmetic. If the connections of one or several ports are broken, the traffic of these ports will
be transmitted on the normal ports, so as to guarantee the connection reliability.
Depending on different aggregation modes, aggregation groups fall into two types: Static LAG
and LACP Config. The LAG function is implemented on the LAG Table, Static LAG and LACP
Config configuration pages.
5.2.1 LAG Table
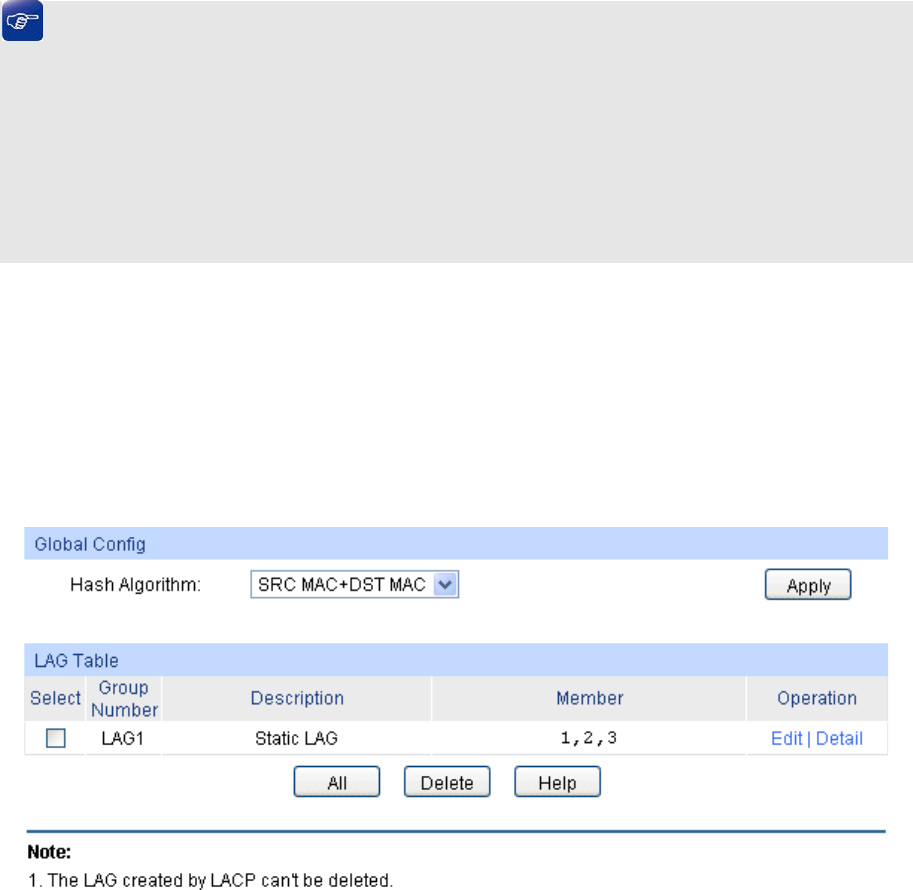
On this page, you can view the information of the current LAG of the switch.
Choose the menu Switching → LAG → LAG Table to load the following page.
Figure 5-6 LAG Table
51





















