Chapter 5 - Synchronous Mode Operation
5-2
Clock Options
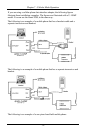
Synchronous data must be transmitted and received with a common timing clock.
This timing clock is used to transmit data from the DTE to the modem which
modulates the data according to this clock. The receiving modem recovers the
clock and data from the carrier and sends the data to the receiving DTE along
with the clock. There are three types of transmission synchronous clock sources to
choose from:
1. The internal clock is the one that suits most applications and is the default; in
this case, the clock signal is generated by the sending modem.
2. The slave clock is used when in remote digital loopback mode.
3. The external clock is a signal generated by the sending DTE.
INTERNAL AT&X0 The modem provides the clock and sends it to the
DTE. Adaptive rate can be used. (Default)
EXTERNAL AT&X1 The DTE provides the clock and sends it to the
modem. Must use auto-retrain, cannot use adaptive
rate.
SLAVE AT&X2 Recovered receiver clock serves as transmission
clock.
RTS Options
There are two RTS options. The choice depends on application and host/terminal
requirements. In asynchronous mode RTS is used as a hardware flow control
signal.
IGNORED AT&R1 RTS is ignored; always assumed to be ON.
(Default)
CTS TRACKS RTS AT&R0 Delay before CTS responds to RTS's
change. The delay is set in the S26 register.
Command State Options
For synchronous data communication, there are two options you can choose from
to define how the modem will operate in the command state.
SYNC DATA AT&M1 The modem accepts asynchronous command in
command state, but exchanges data
synchronously in data state.
SYNC AT&M3 The modem accepts synchronous command
(V.25bis) and exchanges data synchronously
with a remote modem.