2-13
Cisco ICS 7750 Administration and Troubleshooting Guide
78-10169-02 Rev. B0
Chapter 2 Monitoring the System
SNMP Basics
On the Cisco ICS 7750, the ICS System Manager software (the NMS) typically
sends SNMP requests to a single IP address to access the SNMP MIBs of any
system component. The SNMP agent can then respond to MIB-related queries
being sent by the NMS. Similarly, if CiscoWorks2000 is the NMS, it uses the MIB
variables to set device variables and poll devices on the network. You can then
display the data that CiscoWorks2000 collects as a graph and analyze it to
enhance network performance, to monitor traffic loads, or to troubleshoot
problems. (See “Monitoring with CiscoWorks2000” on page 2-17.)
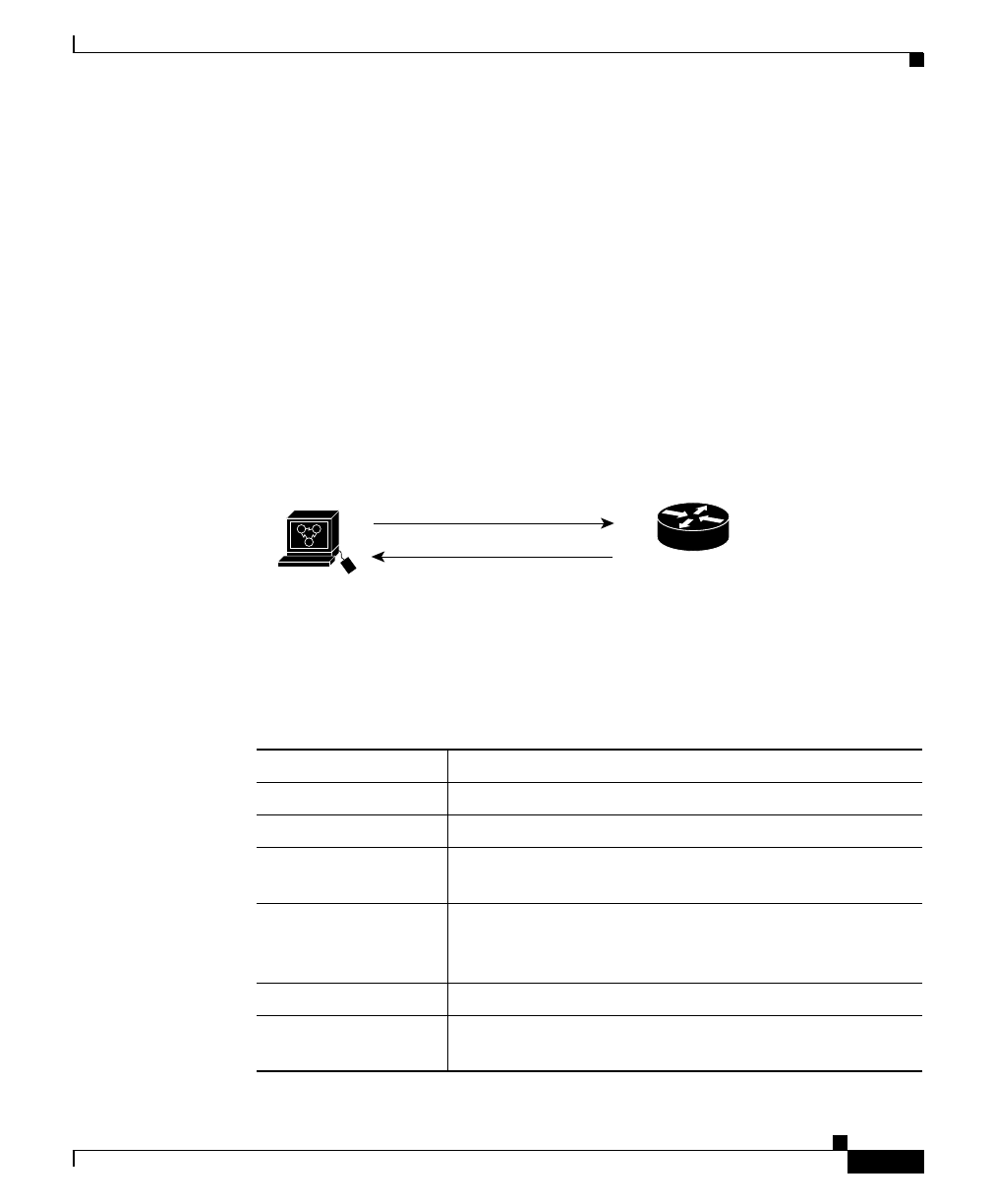
As Figure 2-2 shows, the SNMP agent gathers data from the MIB, which is the
repository for information about device parameters and network data. The agent
can send traps (see “Understanding Traps” on page 2-14) to the manager.
Figure 2-2 SNMP Network
The SNMP manager uses information in the MIB to perform the operations
described in Table 2-6.
Get-request, Get-next-request,
Get-bulk, Set-request
Network device
Get-response, traps
S1203a
SNMP Manager
NMS
MIB
SNMP Agent
Table 2-6 SNMP Manager Operations
Operation Description
get-request Retrieves a value from a specific variable.
get-next-request Retrieves a value from a variable within a table.
get-response The reply to a get-request, get-next-request, and
set-request sent by an NMS.
get-bulk (SNMP version 2 only.) Retrieve large blocks of data,
such as multiple rows in a table, which would otherwise
require the transmission of many small blocks of data.
set-request Stores a value in a specific variable.
trap An unsolicited message sent by an SNMP manager
indicating that some event has occurred.


















