58 Chapter 7
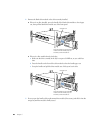
m installing the Apple Fibre Channel PCI Card in a host system and connecting it to the
Xserve RAID system using fibre channel cables
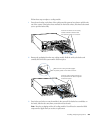
m connecting to an Ethernet network
You use the RAID Admin software to configure RAID storage on your system. Use the Xserve
RAID CD, supplied with the system, to install RAID Admin on any computer or server that
you want to use for remote administration of the system. See the document “Using RAID
Admin and Disk Utility” on the CD that came with your system for details.
About RAID Storage
RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a data-storage technology that spreads
data across multiple drives. This technology provides several benefits over a single large hard
disk, including
m data redundancy for protection and availability
m higher performance as a result of reading or writing on several drives simultaneously
m scalability for expansion of storage
These benefits are especially useful in a server environment where downtime is very
expensive, drive performance is critical to server performance, and the opportunity to
increase storage capacity quickly and easily is essential.
How RAID Works
In a RAID system, either a hardware controller or software manages the reading and writing
of data. The Xserve RAID system uses two hardware controllers, which each manage up to
seven drive modules. By segmenting and writing or reading data on multiple drives
simultaneously, the RAID controller achieves fast and highly efficient storage and access.
The controller can also duplicate all information stored for maximum data protection.
Another protection method, parity, provides the ability to rebuild data. Parity protects stored
information without requiring data duplication. When data is protected by duplication or
parity, it is still available if a drive fails. Duplicated data is simply retrieved from the second
storage site; parity-protected data is reconstructed using the parity formula. You can remove
and replace a failed disk (known as “hot swapping”), and the controller then rebuilds the
data using the information on the remaining drives.
The way the controller stores and retrieves data on the Xserve RAID system is determined by
the RAID level and storage method you choose. See “Data Storage Methods” on page 59 and
“RAID Levels” on page 60 for more information about these choices.