INTRODUCTION
27
1.7.3 RAID 1E
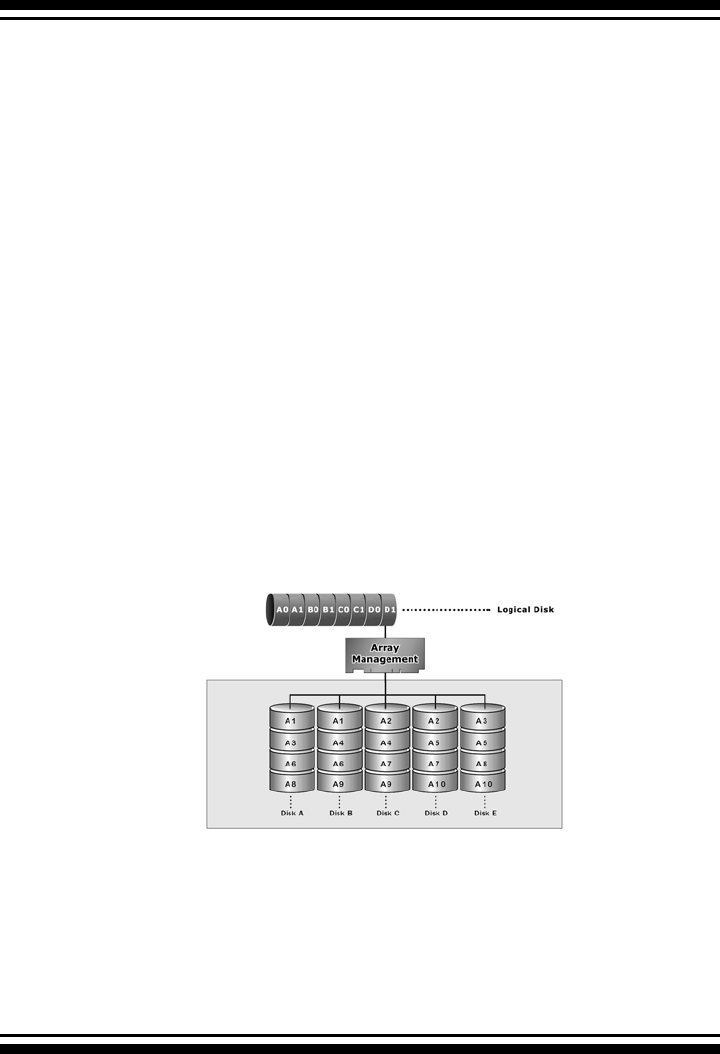
RAID 1E is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1, combing strip-
ping with disk mirroring. RAID Level 1E combines the fast per-
formance of Level 0 with the data redundancy of Leve1 1. In
this conguration, data is distributed across several disk drives,
similar to Level 0, which are then duplicated to another set of
drive for data protection. RAID 1E has been traditionally imple-
mented using an even number of disks, some hybrids can use an
odd number of disks as well. Illustration is an example of a hy-
brid RAID 1E array comprised of ve disks; A, B, C, D and E. In
this conguration, each strip is mirrored on an adjacent disk with
wrap-around. In fact this scheme - or a slightly modied version
of it - is often referred to as RAID 1E and was originally proposed
by IBM. When the number of disks comprising a RAID 1E is even,
the striping pattern is identical to that of a traditional RAID 1E,
with each disk being mirrored by exactly one other unique disk.
Therefore, all the characteristics for a traditional RAID 1E apply
to a RAID 1E when the latter has an even number of disks. Areca
RAID 1E offers a little more exibility in choosing the number of
disks that can be used to constitute an array. The number can be
even or odd.
1.7.4 RAID 3
RAID 3 provides disk striping and complete data redundancy
though a dedicated parity drive. RAID 3 breaks up data into
smaller blocks, calculates parity by performing an exclusive-or
on the blocks, and then writes the blocks to all but one drive in