INTRODUCTION
28
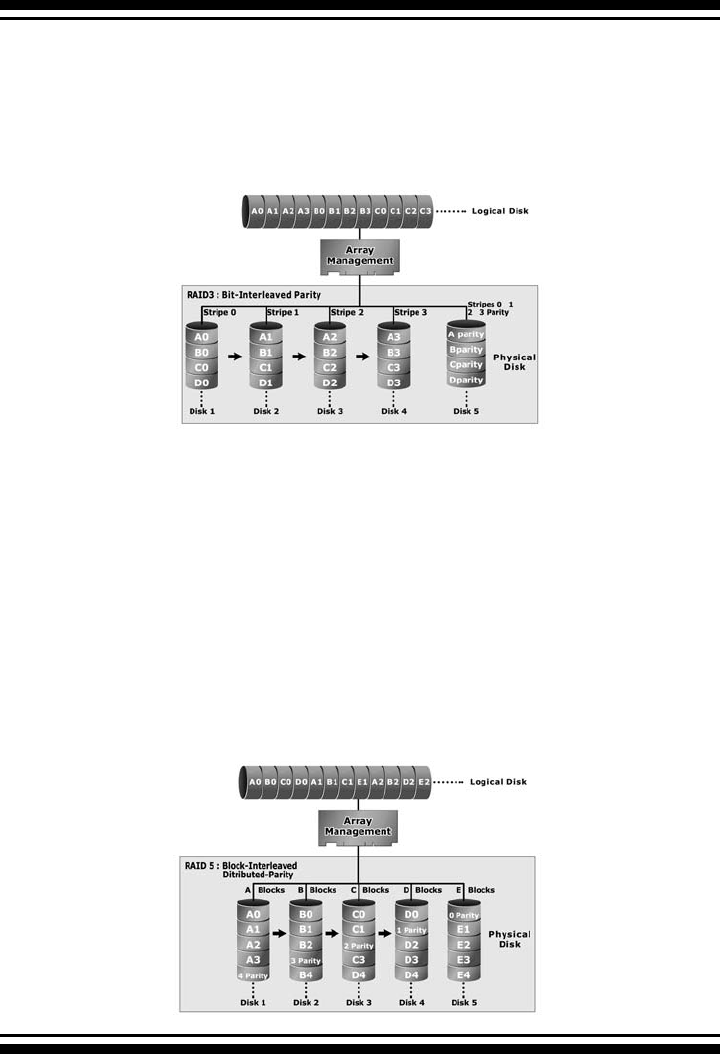
1.7.5 RAID 5
RAID 5 is sometimes called striping with parity at byte level. In
RAID 5, the parity information is written to all of the drives in the
controllers rather than being concentrated on a dedicated parity
disk. If one drive in the system fails, the parity information can
be used to reconstruct the data from that drive. All drives in the
array system can be used for seek operations at the same time,
greatly increasing the performance of the RAID system. This
relieves the write bottleneck that characterizes RAID 4, and is the
primary reason that RAID 5 is more often implemented in RAID
arrays.
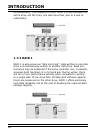
the array. The parity data created during the exclusive-or is then
written to the last drive in the array. If a single drive fails, data is
still available by computing the exclusive-or of the contents cor-
responding strips of the surviving member disk. RAID 3 is best
for applications that require very fast data- transfer rates or long
data blocks.