20020601
English
í Equipment
Two carts of identical mass String Pulley with a bracket to secure it
Velcroă 500g weight Cushion
Distance Measurement Setup (EA-200, graphic scientific calculator, data communication
cable, optional EA-2*
1
)
í Preparing the Carts
u Measure the masses of Cart 1 and Cart 2.
u Affix Velcroă to the impact surfaces of Cart 1 and Cart 2.
u Use tape to securely affix the string to the center of the front end (the same end where
the Velcroă is affixed) of Cart 1.
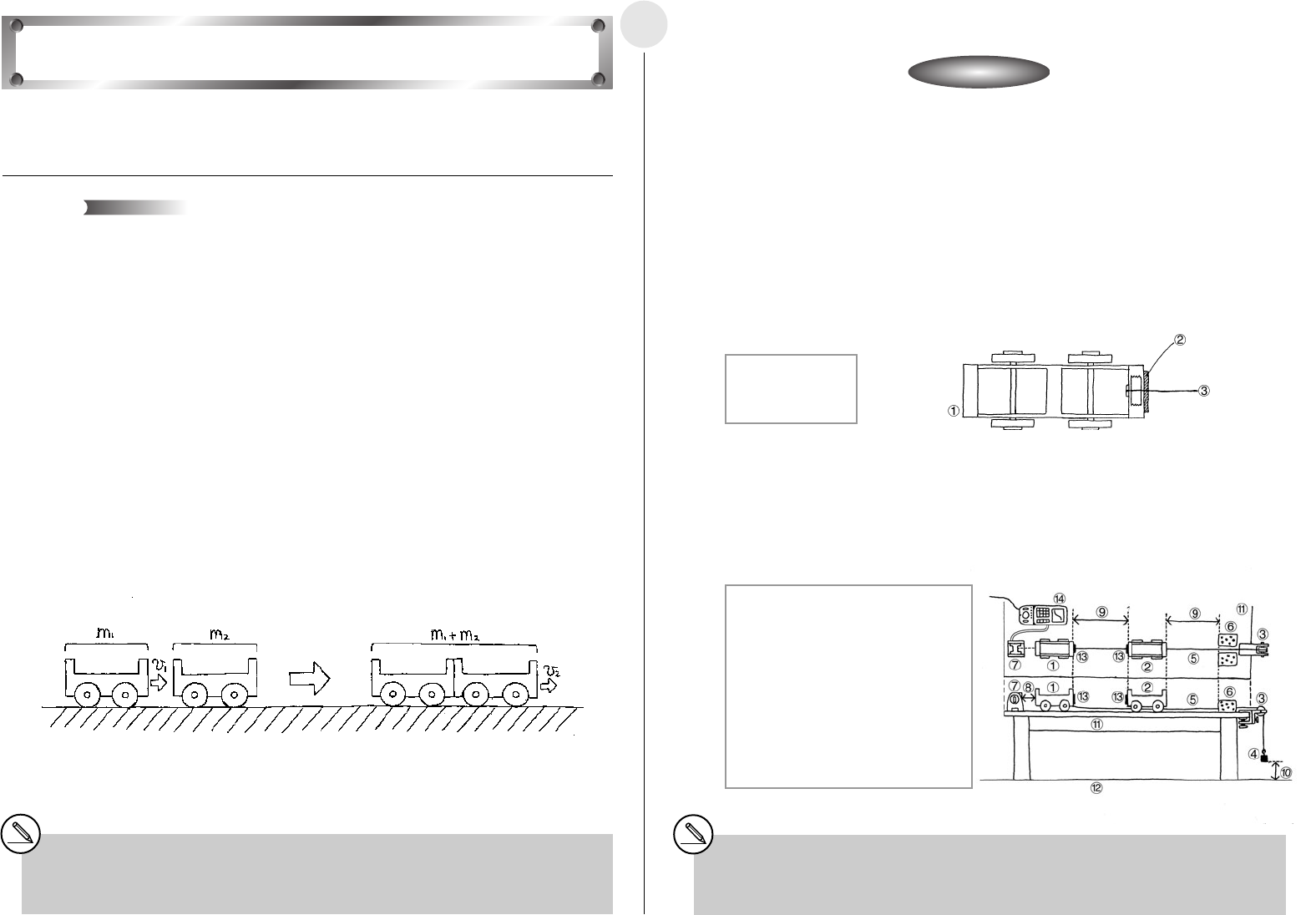
í Setting Up
u Align the EA-2, Cart 1, Cart 2 and the pulley in a straight line.
u Run the string under Cart 2 and place it onto the pulley. Attach the weight to the end of
the string.
u Support the weight with your hand so it does not pull Cart 1.
2-3-1
The purpose of this activity is to investigate the law of conservation of momentum through
the collision of two carts.
Collisions can take on many different forms, and can involve automobiles, locomotives,
shopping carts, or even two people. The force of the impact when the two objects collide
depends not only on their velocities but also their respective masses (weight), and you can
calculate the momentum of an object by multiplying its mass by its velocity.
Despite the variables involved, one principle always holds true – if external forces such as
friction are ignored, the sum of the momenta of two objects prior to collision is the same as
the sum of the momenta of the objects after collision. This is the principle known as the
“conservation of momentum.” This principle is an excellent tool for understanding the
dynamics of collisions.
The following expresses conservation of momentum in the case of a stationary cart being
struck by another cart, after which the two carts adhere to each other and continue in
motion together.
m
1
v
1
= (m
1
+ m
2
)v
2
m
1
(kg) : Mass of Cart 1
m
2
(kg) : Mass of Cart 2
v
1
(m/s): Velocity of Cart 1 Before Collision
v
2
(m/s): Velocity of Two Carts After Collision
This means that when the two carts are of identical mass, the combined velocity of the two
carts after collision is one half that of the velocity of Cart 1 before the collision.
Conservation of Momentum
Theory
The above expression can be used to obtain the post-collision velocity of two carts (while they
adhere to each other) of different masses.
1 Back of Cart 1
2 String
3 Velcroă
1 Cart 1
2 Cart 2
3 Pulley
4 500g weight
5 String
6 Cushions
7 EA-2 (SONIC)
8 Allow 60cm
between EA-2
and Cart 1.
Activity: SetupActivity: Setup
9 Distance: 50cm
0 Height of weight
from floor: 30cm
! Desk
@ Floor
# Velcroă
$ EA-200
*
1
When using the EA-200 in combination with the optional ‘‘Motion Sensor (EA-2) ”, be sure to
power the EA-200 using its bundled AC adaptor (AD-A60024).
*
1
