20020601
English
Activity: SetupActivity: Setup
2-6-1
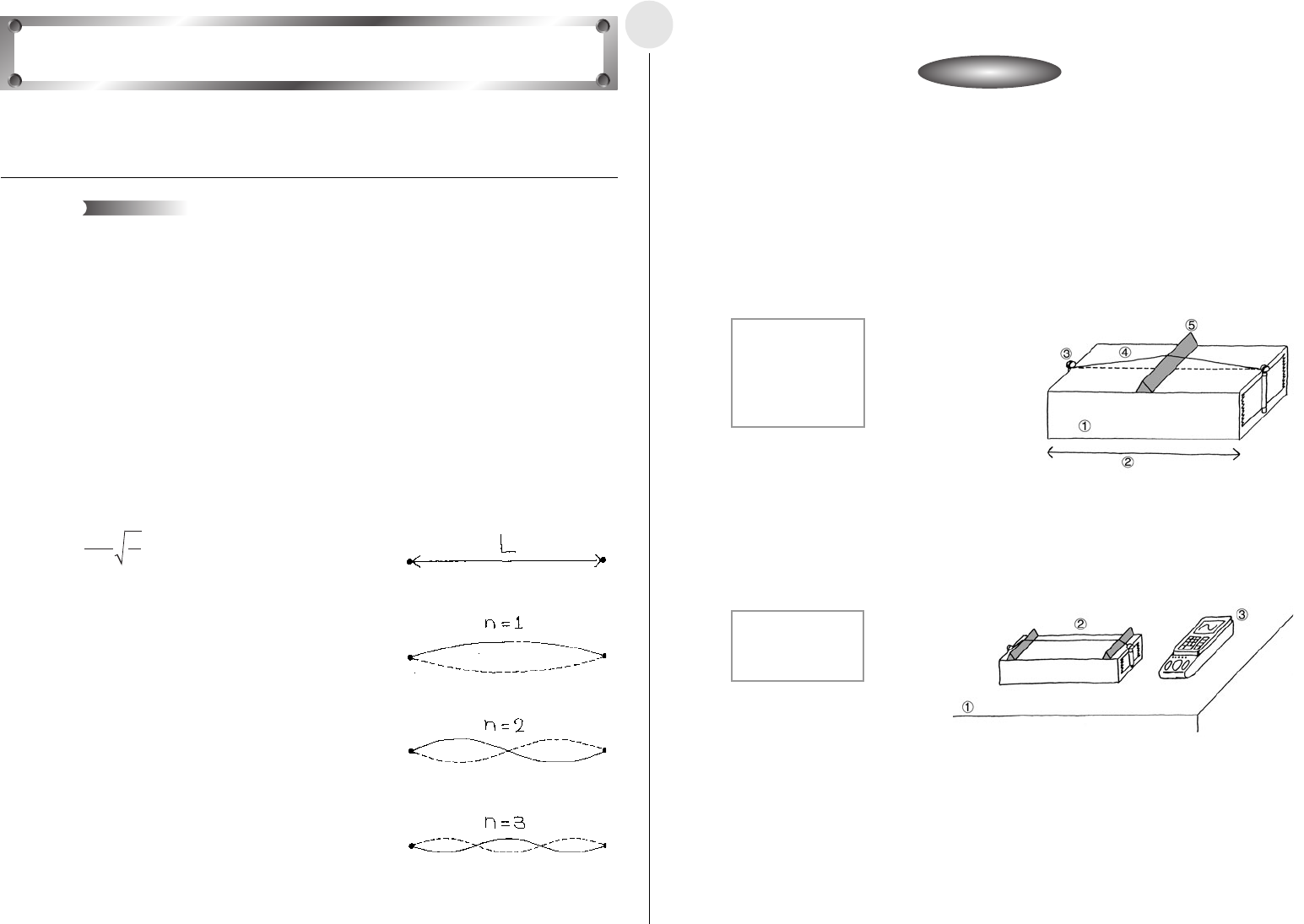
í Equipment
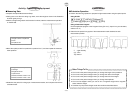
Box String Bolts (2) Triangular Wood Blocks (2)
Audio Measurement Setup (EA-200, graphic scientific calculator, data communication
cable)
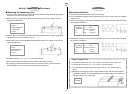
í Building a Monochord
u Use tape to affix the bolts at either end of the box, and stretch the string taut between
them.
u Insert a triangular wood block between the string and the box.
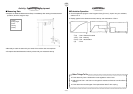
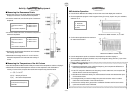
í Setting Up
u Insert two wood blocks between the string and box, and set the monochord on a table or
desk.
u Position the Audio Measurement Setup where it can pick up the sound from the
monochord.
This activity investigates sounds produced in accordance with the natural frequencies of
objects we use in everyday life. It also studies the characteristics of frequencies.
Hitting, striking, plucking, or otherwise disturbing just about any object will cause it to
vibrate. Dropping a pencil or ruler to the floor, or plucking a banjo string will cause it to
vibrate. The sound produced when you blow over the top of a bottle is the air inside of it
vibrating. The vibration of an object tends to occur at a particular frequency or a particular
set of frequencies, which is the “natural frequency” of the object.
Though the strength of the strike, pluck, or other disturbance applied to an object affects the
frequency of the sound produced, in most cases the sound produced is a louder version of
the natural frequency. Generally, the sound produced by an object is the result of multiple
natural frequency sound waves superimposed on each other.
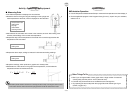
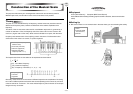
The expression below provides the natural frequency of a string that is fixed at both ends. In
this case, all of the natural frequencies are integer multiples of f
1, which is called the
“fundamental frequency.” The fundamental frequency is the lowest possible frequency at
which an object can vibrate freely.
f
n
(Hz) : String Natural Frequency (n = 1, 2, 3 ...)
L(m) : String Length
S(N) : String Tension
ρ
(kg/m) : String Linear Density (per meter)
Natural Frequency and Sound
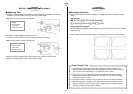
Theory
f
n
=
S
ρ
n
2L
1 Box
2 Box Length: 50cm
3 Bolt
4 String
5 Block
1 Desk
2 Monochord
3 EA-200