CRADLEPOINT MBR1400| USER MANUAL Firmware ver. 3.4.1
© 2012 CRADLEPOINT, INC. PLEASE VISIT HTTP://KNOWLEDGEBASE.CRADLEPOINT.COM/ FOR MORE HELP AND RESOURCES PAGE 69
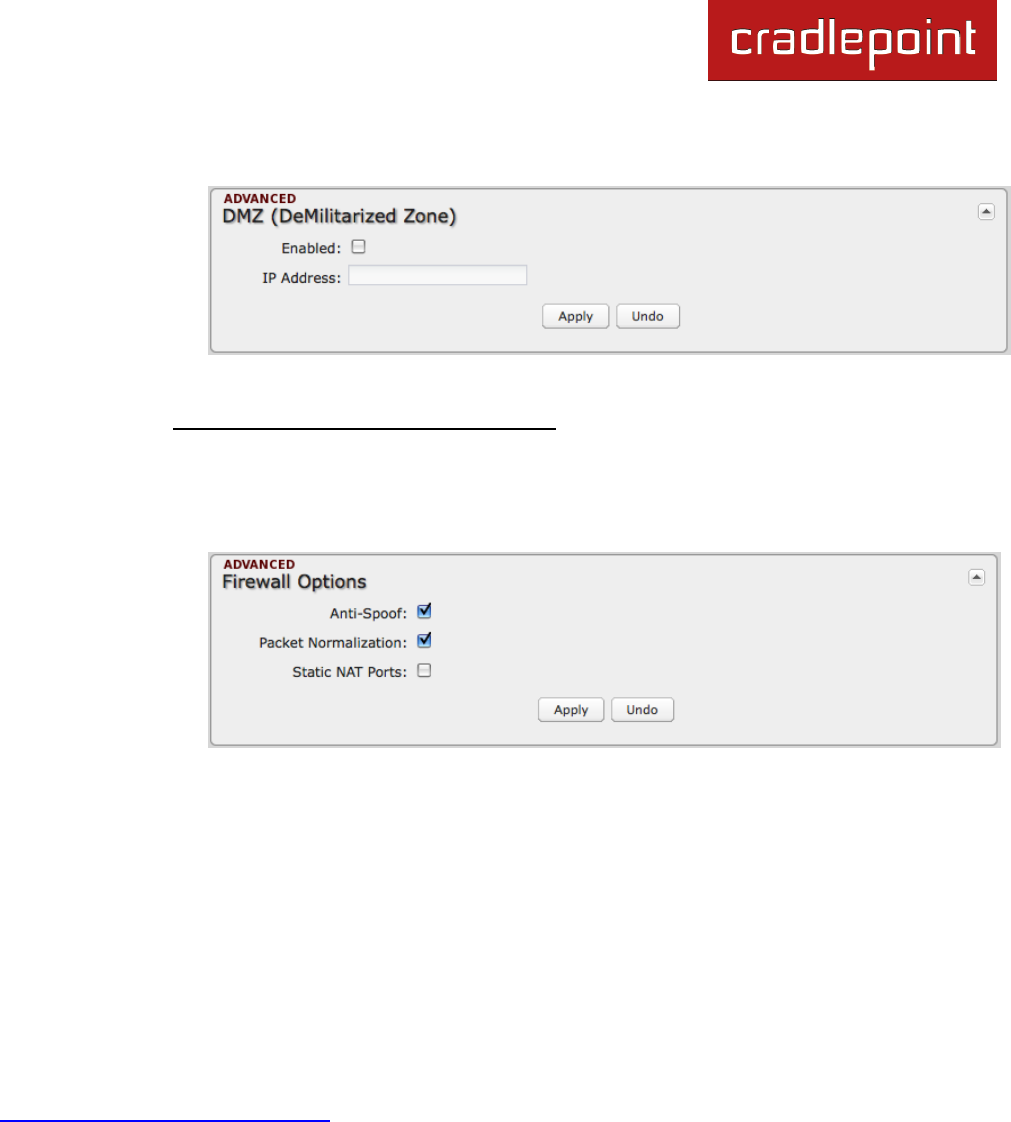
6.4.3 DMZ: DeMilitarized Zone (Advanced)
A DMZ host is effectively not firewalled in the
sense that any computer on the Internet may
attempt to remotely access network services at the
DMZ IP address. Typical uses involve running a
public Web server or sharing files.
Input the IP Address of a single device in your
network to create a DeMilitarized Zone for that device. To ensure that the IP address of the selected device remains
consistent, go to the ―Reservations‖ section under Network Settings → DHCP Server and reserve the IP address for the
device.
As with port forwarding, use caution when enabling the DMZ feature as it can threaten the security of your
network. Only use DMZ as a last resort.
6.4.4 Firewall Options (Advanced)
Anti-Spoof: Anti-Spoof checks help protect against
malicious users faking the source address in
packets they transmit in order to either hide
themselves or to impersonate someone else. Once
the user has spoofed their address they can launch
a network attack without revealing the true source
of the attack or attempt to gain access to network services that are restricted to certain addresses.
Packet Normalization: Normalizing packets helps secure the router in untrusted environments. It does so by "scrubbing"
packets that are ambiguous or might represent a break-in attempt. Packet Normalization also helps insure reliable
connectivity for some WAN devices such as WiMAX modems. Only disable this option if you are sure you do not need it.
Static NAT Ports: If enabled the source port does not translate in TCP and UDP packets during NAT. Some NAT
traversal protocols such as STUN(T) require that the source port stay the same when traversing the firewall.