DES-3226 NWay Standalone Fast Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
• Egress port – A port on a switch where packets are flowing out of the switch, either to
another switch or to an end station, and tagging decisions must be made.
IEEE 802.1Q (tagged) VLANs are implemented on the DES-3226. 802.1Q VLANs require tagging, which
enables them to span the entire network (assuming all switches on the network are IEEE 802.1Q-
compliant).
VLANs allow a network to be segmented in order to reduce the size of broadcast domains. All packets
entering a VLAN will only be forwarded to the stations (over IEEE 802.1Q enabled switches) that are
members of that VLAN, and this includes broadcast, multicast and unicast packets from unknown
sources.
VLANs can also provide a level of security to your network. IEEE 802.1Q VLANs will only deliver
packets between stations that are members of the VLAN.
Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging. The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
allow VLANs to work with legacy switches that don’t recognize VLAN tags in packet headers. The
tagging feature allows VLANs to span multiple 802.1Q-compliant switches through a single physical
connection and allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all ports and work normally.
The IEEE 802.1Q standard restricts the forwarding of untagged packets to the VLAN the receiving port
is a member of.
The main characteristics of IEEE 802.1Q are as follows:
• Assigns packets to VLANs by filtering.
• Assumes the presence of a single global spanning tree.
• Uses an explicit tagging scheme with one-level tagging.
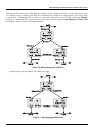
802.1Q VLAN Packet Forwarding
Packet forwarding decisions are made based upon the following three types of rules:
• Ingress rules – rules relevant to the classification of received frames belonging to a VLAN.
• Forwarding rules between ports – decides filter or forward the packet
• Egress rules – determines if the packet must be sent tagged or untagged.
28