Configuration and Management
1/1551-CRH 102 168 Uen Rev A 2008-12-16
23
Authentication is used to restrict access to the wireless network and
encryption is the translation of data into a form that cannot be easily
understood by unauthorized users. The encrypted data can only be sent
and received by users with access to a private encryption key.
Note: Make sure that the operating system(s) and Wireless LAN
interface(s) of the wireless client(s) support the selected
authentication method.
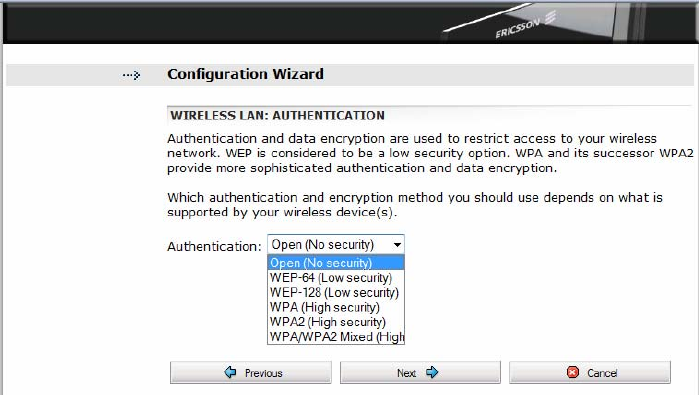
Figure 16 – Wireless LAN: Authentication page
Select one of the authentication methods from the “Authentication” drop-
down list. The available options are as follows:
• Open (No security);
f you select “Open” as authentication method no client configuration is
needed but be aware of that the WLAN will now be open without any
kind of security.
• WEP-64, WEP-128 (Low security);
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is considered to be a low security
option. WEP encrypted data is translated into blocks of either 64 bits
length or 128 bits length.
• WPA, WPA2 (High security);
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and its successor WPA2 are the most
reliable security options. WPA encryption uses the Temporal Key
Integrity Protocol (TKIP) while WPA2 encryption follows the Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES). AES offers a higher level of security and is
approved for sensitive corporate and government data transmission.


















