Operating the Instrument from the Front Panel
Channel Configuration
3
3-9
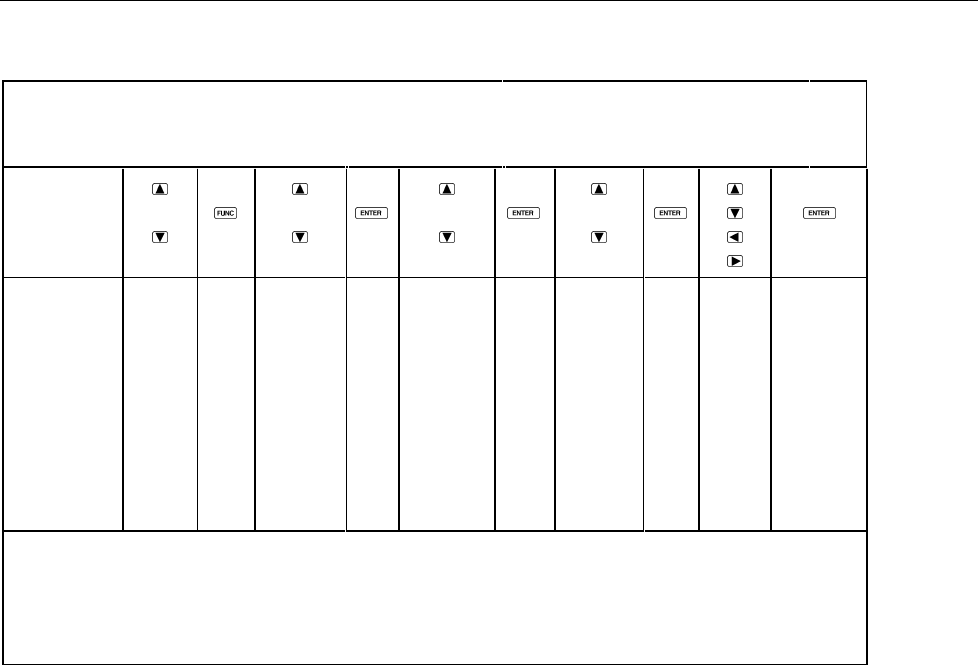
Table 3-6. RTD Temperature
Channel Function
Type
(Note 1)
Terminals
(Note 2)
R0
(Ice Point)
(Note 3)
PRESS
THESE
BUTTONS:
TO
SELECT
FROM
THESE
CHOICES:
0
1
.
.
20
OFF
V DC
V AC
Ω
Hz
°C or °F
J
K
E
T
N
R
S
b
C
Pt
2T
4T
100.00
Completes
selection
and returns
to Inactive
Mode
Note 1. Pt selects RTD temperature measurement (DIN/IEC 751). See Table 3-5 for J, K, E, T, N, R, S, b,
and C thermocouple selections.
Note 2. 4T not available on channels 0 and 11 through 20.
Note 3. R0 default is 100.00
Ω
. A unique R0 value can be set for each channel.
Note
Temperature units can be displayed in degrees Celsius (ºC) or Fahrenheit
(ºF). To switch this setting between ºC and ºF, start with the instrument
powered off, then press and hold B while pressing POWER ON. The
setting can also be changed through the Computer Interface with the
TEMP_CONFIG command (refer to Chapter 4.)
RTD temperature measurement uses a resistance-temperature detector (RTD). RTDs,
while usually larger and more expensive than thermocouples, are frequently used where
accuracy, stability, and repeatability are important. The resistance of an RTD varies
directly with the sensor temperature. Passing a current through this resistance generates a
proportional voltage that can be accurately translated into a temperature reading. The
instrument supports the DIN/IEC 751 RTD type.
Setting Alarms
Alarm Limits
Note
If you press A for a channel that is OFF, an error beep will result.
Therefore, for a new channel, use F to define the channel's measurement
function before selecting A.
Two alarm limits (S and T) can be defined for each analog input channel. An alarm
occurs when the measured value on the channel moves above the HI value or below the
LO value. With the desired channel already selected from Inactive Mode, verify or
change these limits using the procedure shown in Table 3-7. If necessary, refer to
"Entering and Changing Numeric Values" for a more detailed description of the number
changing technique used here.