Getting started Planning the FortiGate configuration
FortiGate-60 Installation Guide 01-28008-0018-20050128 23
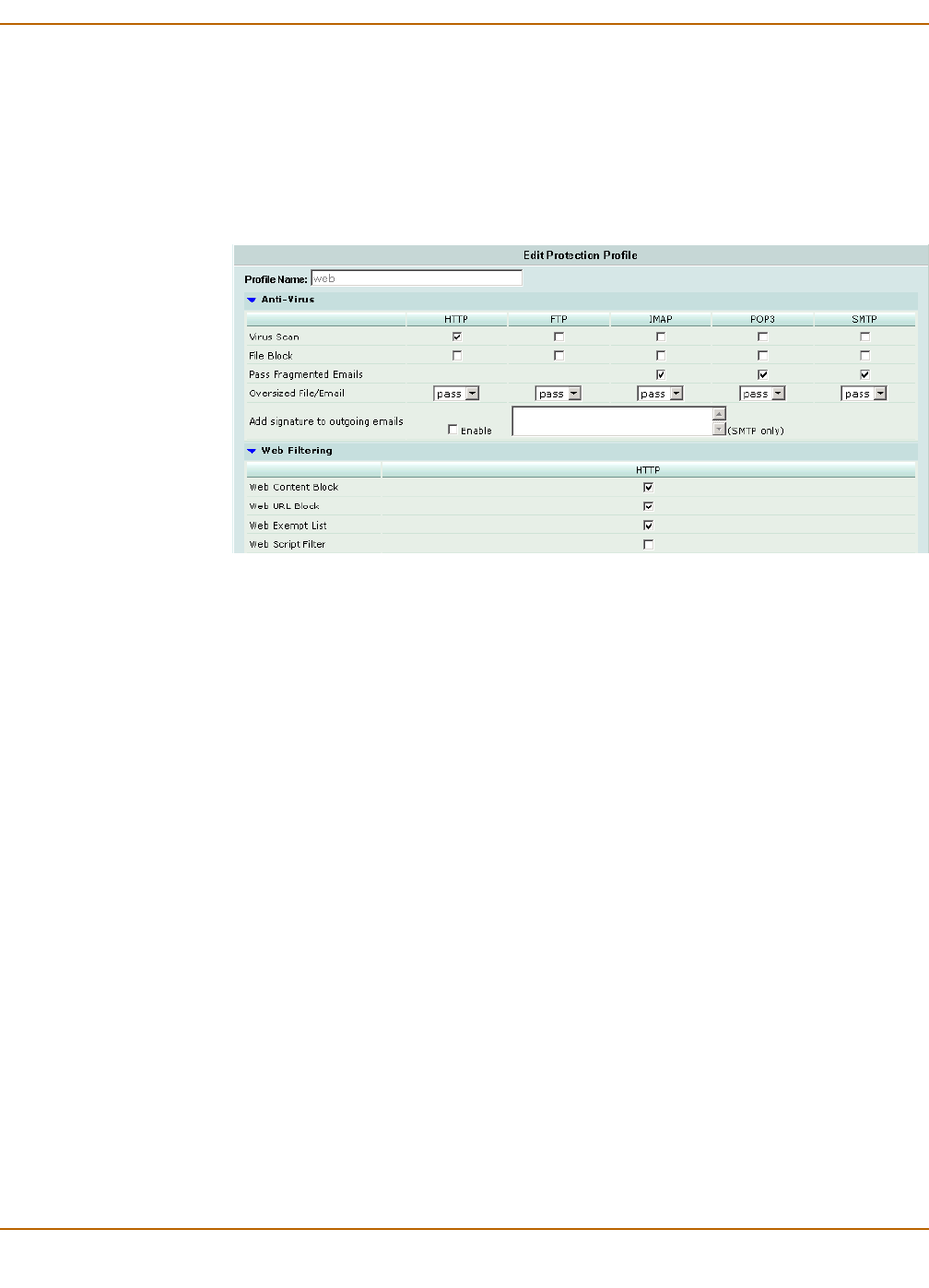
Figure 5: Web protection profile settings
Planning the FortiGate configuration
Before you configure the FortiGate unit, you need to plan how to integrate the unit into
the network. Among other things, you must decide whether you want the unit to be
visible to the network, which firewall functions you want it to provide, and how you
want it to control the traffic flowing between its interfaces.
Your configuration plan depends on the operating mode that you select. The FortiGate
unit can be configured in one of two modes: NAT/Route mode (the default) or
Transparent mode.
You can also configure the FortiGate unit and the network it protects using the default
settings.
NAT/Route mode
In NAT/Route mode, the FortiGate unit is visible to the network. Like a router, all its
interfaces are on different subnets. The following interfaces are available in
NAT/Route mode:
• Internal is the interface to the internal network.
• WAN1 is the default interface to the external network (usually the Internet).
• WAN2 is the redundant interface to the external network.
• DMZ is the interface to the DMZ network.
• Modem is the interface for connecting an external modem to the FortiGate-60. See
“Configuring the modem interface” on page 55
Web To apply antivirus scanning and web content blocking to HTTP content
traffic. You can add this protection profile to firewall policies that control
HTTP traffic.
Unfiltered To apply no scanning, blocking or IPS. Use if you do not want to apply
content protection to content traffic. You can add this protection profile to
firewall policies for connections between highly trusted or highly secure
networks where content does not need to be protected.


















