Data Format
34 C141-E252
3.1.5 Format capacity
The size of the usable area for storing user data on the HDDs (format capacity) varies according to
the logical data block or the size of the spare sector area. Table 3.1 lists examples of the format
capacity when the typical logical data block length and the default spare area are used. The following
is the general formula to calculate the format capacity.
[Number of sectors of each zone] = [number of sectors per track × number of tracks per cell –
number of alternate spare sectors per cell] × [number of cells in the zone]
[Formatted capacity] = [total of sectors of all zones] ÷ [number of physical sectors in logical block] ×
[logical data block length]
The following formula must be used when the number of logical data blocks are specified with the
parameter in the MODE SELECT or MODE SELECT EXTENDED command.
[Format capacity] = [logical data block length] × [number of logical data blocks]
The logical data block length, the maximum logical block address, and the number of the logical data
blocks can be read out by a READ CAPACITY, MODE SENSE, or MODE SENSE EXTENDED
command after initializing the disk.
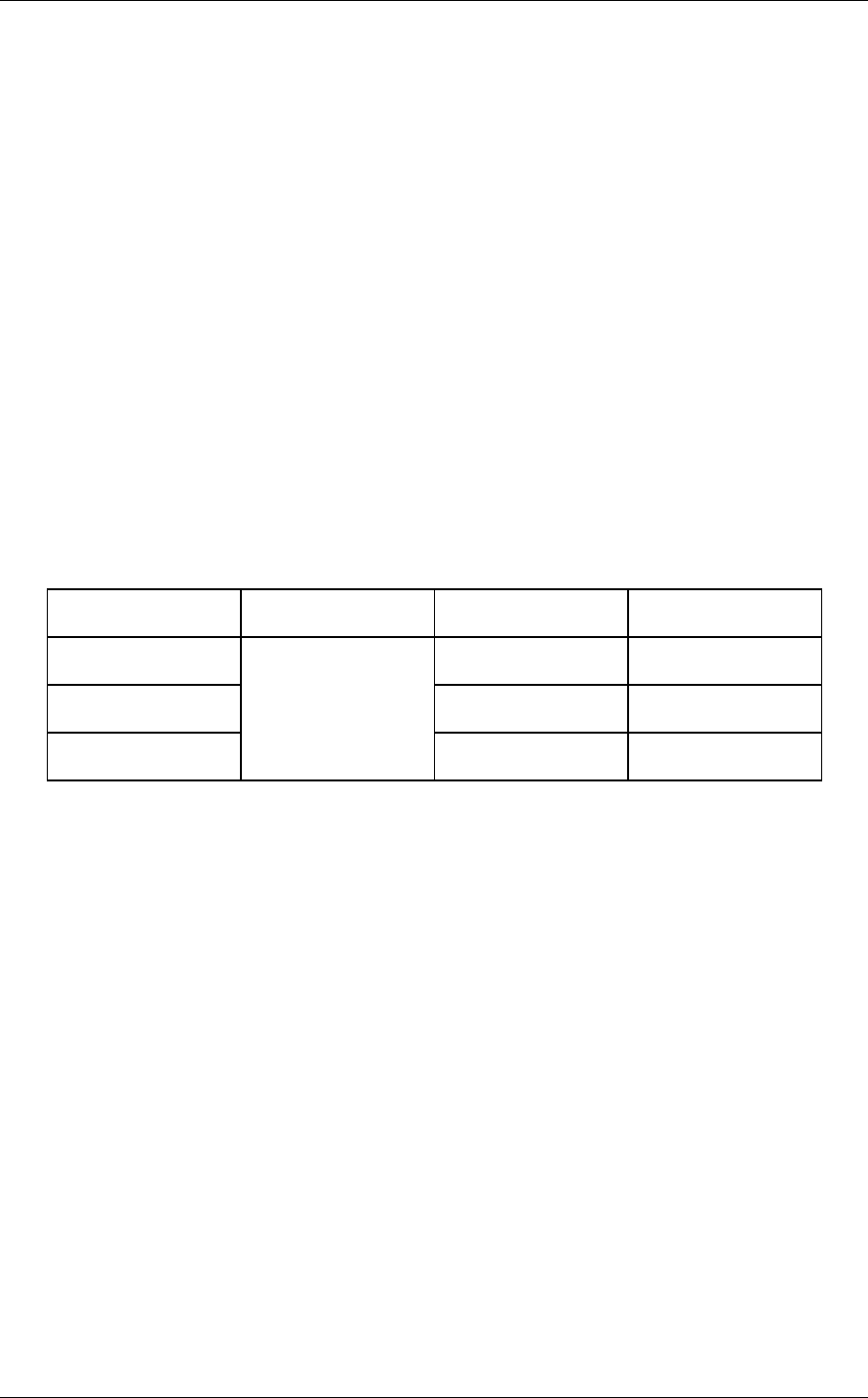
Table 3.1 Format capacity
Model Data block length User blocks Format capacity (GB)
MBA3300RC 585, 937, 500 300 (*)
MBA3147RC 287, 277, 984 147 (*)
MBA3073RC
512
143, 638, 992 73.5 (*)
(*) One gigabyte (GB) = one billion bytes; accessible capacity will be less and actual capacity depends
on the operating environment and formatting.
Note:
Total number of spare sectors is calculated by adding the number of spare sectors in each primary
cylinder and the number of sectors in the alternate cylinders.
3.2 Logical Data Block Addressing
The HDDs relate a logical data block address to each physical sector at formatting. Data on the disk
is accessed in logical data block units. The initiator specifies the data to be accessed using the logical
data block address of that data.


















