88
LifeBook E Series Notebook - Appendix A
Before Using the Wireless LAN
This manual describes the procedures required to prop-
erly set up and configure the integrated Wireless LAN
Mini-PCI device (referred to as "WLAN device" in the
rest of the manual). Before using the WLAN device, read
this manual carefully to ensure it's correct operation.
Keep this manual in a safe place for future reference.
Wireless LAN Device Covered by this Document
This document is applicable to systems containing one
of the following two devices. Most of the procedures are
identical. Sections that differ between the two devices
have been noted in the text:
■
Intel® PRO/Wireless 3945ABG (WM3945ABG)
Network Connection (802.11a+b/g)
■
Atheros® AR5006EXS (AR5BXB6) Mini-Card
Wireless network card (802.11a+b/g)
Characteristics of the WLAN Device
■
The WLAN device is a Mini-PCI card attached to
the main board of the mobile computer.
■
It operates in two license-free RF bands, therefore
eliminating the need to procure an FCC license to
operate. It operates in the 2.4GHz Industrial,
Scientific, and Medical (ISM) RF band and in the
lower and middle bands of the 5GHz Unlicensed
National Information Infrastructure (UNII)
bands.
■
The WLANs are capable of three operating
modes, IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11b and
IEEE802.11g, wireless LAN standards governed
by the IEEE (Institute of Electronics and Elec-
trical Engineers).
■
Encoding of data is modulated using Direct
Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Comple-
mentary Code Keying (CCK) when the WLAN
device is operating in IEEE 802.11b mode and
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
(OFDM) when operating in IEEE802.11a or
IEEE802.11g mode.
■
The WLAN device is Wi-Fi certified and operates
at the maximum data transfer rate of 54 Mbps in
IEEE802.11a or IEEE802.11g mode and 11 Mbps
in IEEE802.11b mode.
■
The WLAN device supports the following
encryption methods - WEP, TKIP, and AES
encryption.
WIRELESS LAN MODES USING THIS DEVICE
Ad Hoc Mode
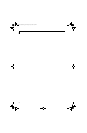
(See Figure A-1) "Ad Hoc Mode" refers to a wireless
network architecture where wireless network connec-
tivity between multiple computers is established without
a central wireless network device, typically known as
Access Point(s). Connectivity is accomplished using only
client devices in a peer-to-peer fashion. That is why Ad
Hoc networks are also known as peer-to-peer networks.
Ad Hoc networks are an easy and inexpensive method
for establishing network connectivity between multiple
computers.
Ad Hoc mode requires that the SSID, network authenti-
cation, and encryption key settings are identically
configured on all computers in the Ad Hoc network.
Access Point (Infrastructure) Mode
(See Figure A-2) Infrastructure mode refers to a wireless
network architecture in which devices communicate
with wireless or wired network devices by communi-
cating through an Access Point. In infrastructure mode,
wireless devices can communicate with each other or
with a wired network. Corporate wireless networks
operate in infrastructure mode because they require
access to the WLAN in order to access services, devices,
and computers (e.g., file servers, printers, databases).
Figure A-1. Ad Hoc Mode Network
Eagle E8310.book Page 88 Thursday, May 3, 2007 2:55 PM