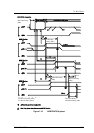
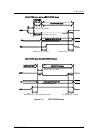
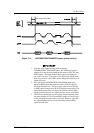
SCSI BUS
7-28 C156-E228-02EN
(1) Asynchronous transfer
In asynchronous transfer mode, information transfer is controlled by the INIT and
TARG which are checking the status transition (from false to true and vice versa)
of REQ and ACK signals (interlock type). Asynchronous transfer can be used in
all types of INFORMATION TRANSFER phase (COMMAND, DATA,
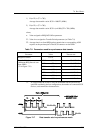
STATUS, MESSAGE). Figure 7.14 shows the timing rule of the asynchronous
transfer.
a. Transfer from TARG to INIT
The TARG specifies the information transfer direction by the I/O signal. If
the I/O signal is true, the information on the DATA BUS is transferred from
the TARG to the INIT. Information transfer processing is as follows:
1) The TARG asserts the REQ signal at least Deskew Delay + Cable Skew
Delay after sending valid information on the data bus (DB7 to DB0, P).
It must maintain the state of DB7 to DB0, P until the ACK signal
becomes true on the TARG.
2) INIT fetches the data from the data bus (DB7 to DB0, P) after the REQ
signal becomes true. It asserts the ACK signal to report the completion
of reception.
3) After the ACK signal becomes true on the TARG, the TARG negates the
REQ signal. Thereafter, the TARG can change the data of the data bus.
4) The INIT negates the ACK signal after the REQ signal becomes false.
5) After the ACK signal becomes false, the TARG proceeds to transfer the
next byte.
b. Transfer from INIT to TARG
When the I/O signal is false, information on the data bus is transferred from
the INIT to the TARG. Information transfer processing is as follows.
1) The TARG asserts the REQ signal to request the INIT to send
information.
2) The INIT asserts the ACK signal at least Deskew Delay + Cable Skew
Delay after sending valid information of the requested type on the data
bus (DB7 to DB0, P). The information on the DATA BUS must be
maintained until the REQ signal becomes false on the INIT.
3) The TARG fetches data from the data bus (DB7 to DB0, P) after the
ACK signal becomes true and negates the REQ signal to report the
completion of reception.
4) When the REQ signal becomes false on the INIT, the INIT negates the
ACK signal. After that, the INIT can change data on the data bus.
5) The TARG proceeds to the transfer of the next byte after the ACK signal
becomes false.