Entering and Evaluating Equations 6-11
To evaluate an equation:
1. Display the desired equation. (See "Displaying and Selecting Equations"
above.)
2. Press
or . The equation prompts for a value for each variable
needed. (If the base of a number in the equation is different from the current
base, the calculator automatically changes the result to the current base.)
3. For each prompt, enter the desired value:
If the displayed value is good, press
.
If you want a different value, type the value and press . (Also see
"Responding to Equation Prompts" later in this chapter.)
To halt a calculation, press or . The message is shown in
line 2.
The evaluation of an equation takes no values from the stack — it uses only numbers
in the equation and variable values. The value of the equation is returned to the X–
register.
Using ENTER for Evaluation
If an equation is displayed in the equation list, you can press to evaluate
the equation. (If you're in the process of typing the equation, pressing
only
ends the equation — it doesn't evaluate it.)
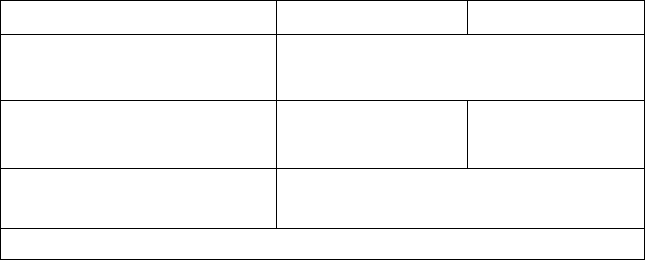
Type of Equation Result for Result for
Equality: g(x) = f(x)
Example: x
2
+ y
2
= r
2
g(x) – f(x)
x
2
+ y
2
– r
2
Assignment: y = f(x)
Example: A = 0.5 × b x h
f(x)
0.5 × b × h
y – f(x)
A – 0.5 × b × h
Expression: f(x)
Example: x
3
+ 1
f(x)
x
3
+ 1
Also stores the result in the left–hand variable, A for example.
