12-8 Statistical Operations
L.R. (Linear Regression) Menu
To find an estimated value for x (or y), key in a given hypothetical value for y
(or x), then press
() (or Õ ().
To find the values that define the line that best fits your data, press
followed by , , or .
Example: Curve Fitting.
The yield of a new variety of rice depends on its rate of fertilization with nitrogen.
For the following data, determine the linear relationship: the correlation coefficient,
the slope, and the y–intercept.
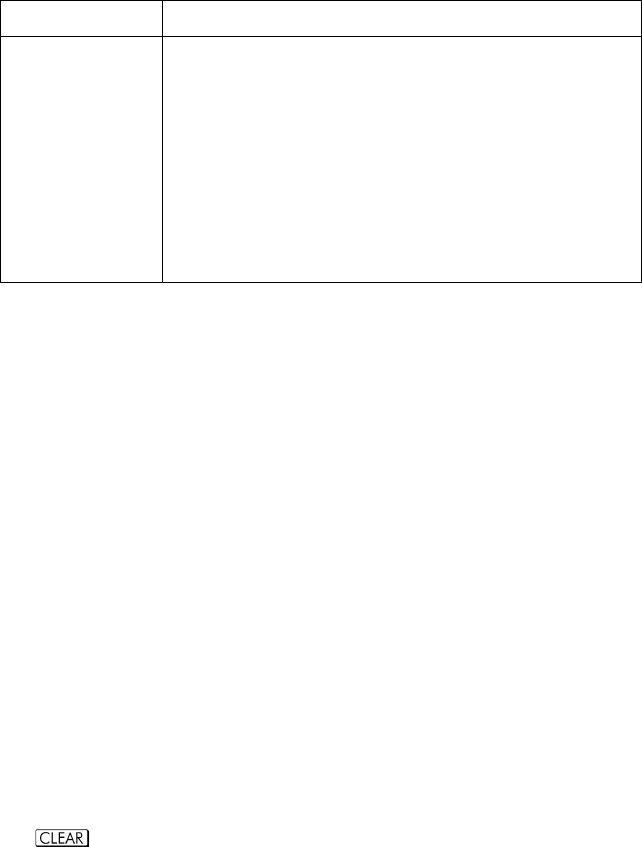
Menu Key Description
Estimates (predicts) x for a given hypothetical value of y,
based on the line calculated to fit the data.
Estimates (predicts) y for a given hypothetical value of x,
based on the line calculated to fit the data.
Correlation coefficient for the (x, y) data. The correlation
coefficient is a number in the range –1 through +1 that
measures how closely the calculated line fits the data.
Slope of the calculated line.
y–intercept of the calculated line.
X, Nitrogen Applied
(kg per hectare)
0.00 20.00 40.00 60.00 80.00
Y, Grain Yield
(metric tons per hectare)
4.63 5.78 6.61 7.21 7.78
Keys: Display: Description:
()
Clears all previous statistical
data.
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
