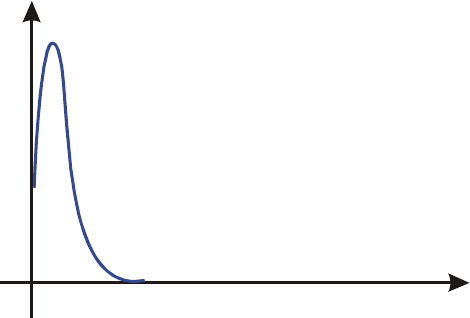
More about Integration E-5
The graph is a spike very close to the origin. Because no sample point happened to
discover the spike, the algorithm assumed that f(x) was identically equal to zero
throughout the interval of integration. Even if you increased the number of sample
points by calculating the integral in SCI 11 or ALL format, none of the additional
sample points would discover the spike when this particular function is integrated
over this particular interval. (For better approaches to problems such as this, see the
next topic, "Conditions That Prolong Calculation Time.")
Fortunately, functions exhibiting such aberrations (a fluctuation that is
uncharacteristic of the behavior of the function elsewhere) are unusual enough that
you are unlikely to have to integrate one unknowingly. A function that could lead to
incorrect results can be identified in simple terms by how rapidly it and its low–order
derivatives vary across the interval of integration. Basically, the more rapid the
variation in the function or its derivatives, and the lower the order of such rapidly
varying derivatives, the less quickly will the calculation finish, and the less reliable
will be the resulting approximation.
f (x)
x


















