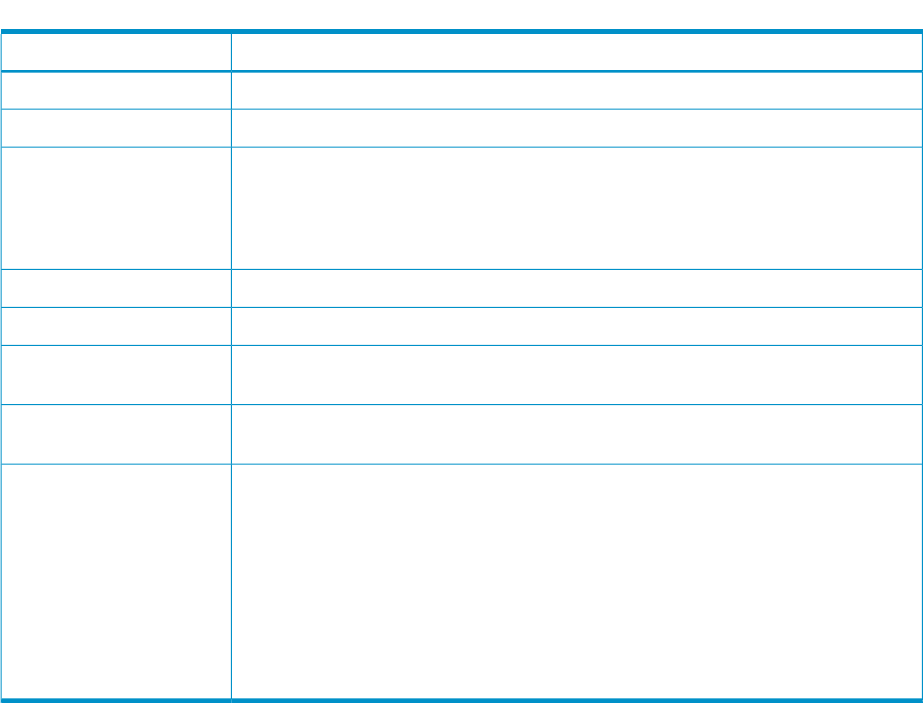
Table 7 HP P6000 Performance Data Collector command modifiers (continued)
DescriptionModifier
Specifies that a time stamp not be included in the CSV output.-nots
Specifies the directory in which the output files from the mof command are saved.-od
Limits array data collection to the specified arrays. You must enter at least one array and
you can use this modifier with any command. When specifying arrays, you can use
-szarray [array]*
either the array's WWN or friendly name. For example, if you enter evaperf as -sz
server1 server3, data is displayed for arrays server1 and server3 only. If you do
not include this modifier, data is collected from all arrays visible to the host.
Displays TLC-compliant data for the mof command.-tlc
Displays output in tab-separated variable (TSV) format with a time stamp.-tsv
Adds a time stamp to the -csv output in the following format: Fri Jul 23 16:23:05
2004.
–ts1
Adds a time stamp to the -csv output in the following format: 23/Jul/2004 16:23:05
2004. This is the default format.
-ts2
Display times in microseconds (the default is milliseconds). Latencies are displayed in
milliseconds (ms) by default. Use the -us option to show times in microseconds for more
accuracy.
The -us modifier does not affect the following commands:
-us
• vdrl
• vdrlg
• vdwl
• vdwlg
Using the graphical user interface
This section describes how to display and manage array performance metrics using the graphical
user interface, Windows Performance Monitor, and assumes that you are familiar with the tool.
Windows Performance Monitor does not permit more than one hierarchical object level. Therefore,
objects, such as virtual disks, are grouped as a single list of instances, even though they may be
located on different arrays. The instance name indicates the array on which the virtual disk is
located.
Remote performance monitoring with Windows Performance Monitor is not supported.
The binary logging feature of Windows Performance Monitor is limited in the number of HP array
performance objects it can log simultaneously. Logging works most reliably when you log small
numbers and instances of counters. When the number of counters and instances logged is too
large, nothing is saved in the binary log file.
To display array performance metrics:
Using the graphical user interface 85


















