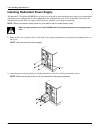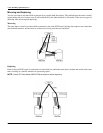
Ch 3: Installing Optional Devices
54 Hitachi PC VisionBase8450H/R Server
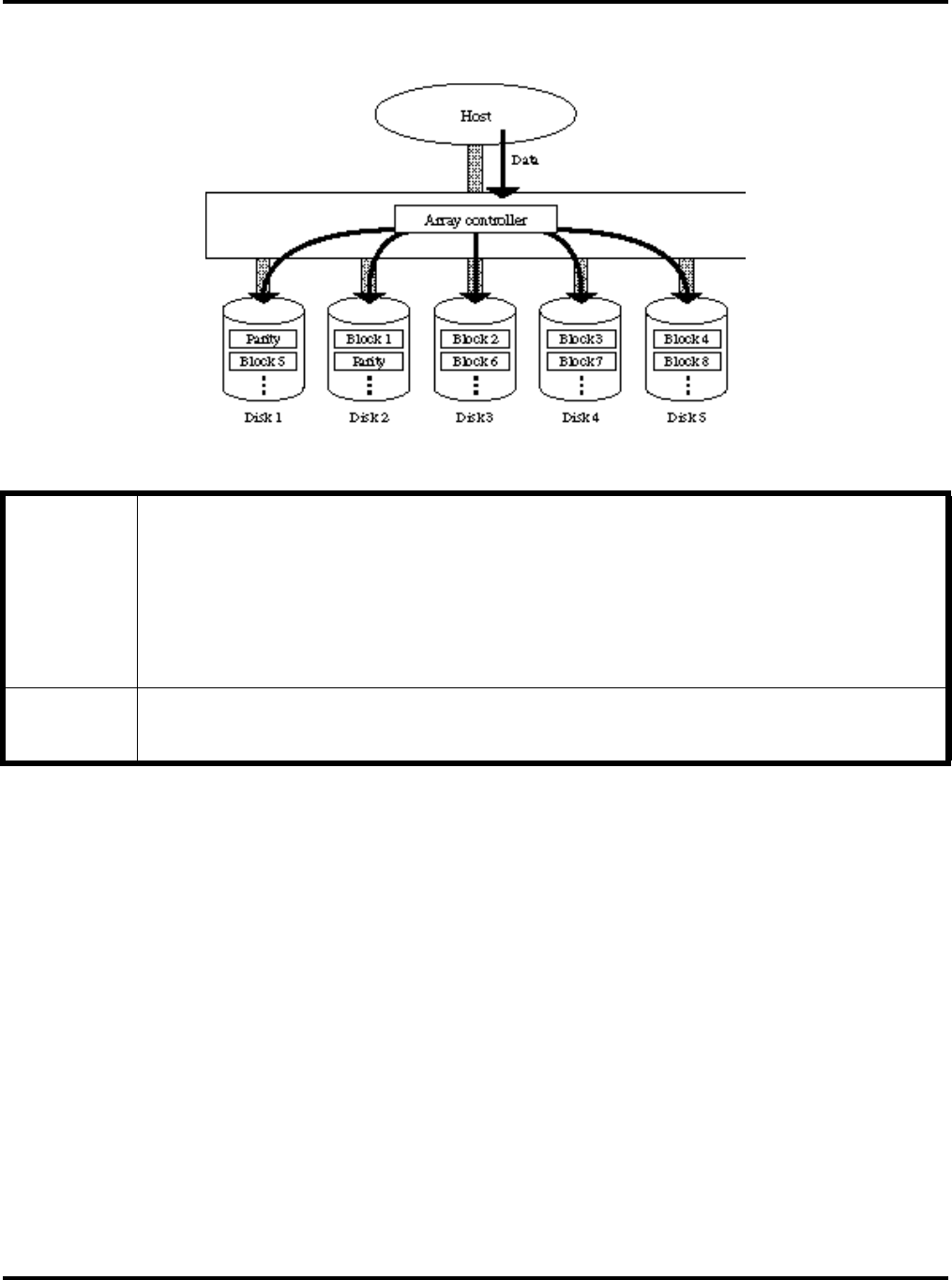
RAID5
Data, together with array parity, is striped in blocks, extending over all hard disks.
Number of hard disks required: 3 (min.) to 6 (max.)
Advantages: • Capacity-to-cost ratio is improved as compared with RAID1.
• Data redundancy is ensured by distributing data to several hard disks; therefore, each hard disk can
perform read/write operation independently. This type of disk array is useful for transaction processing
because data is striped in block.
• If a hard disk within the array fails, the lost data is computed based on the array parities, enabling the read/
write operation to continue. By replacing the hard disk, you can rebuild the data without interrupting your
current task.
• Because array parities are distributed to each hard disk, you can have the advantages of parallel
processing through independent access to the hard disks when writing data.
Disadvantages: • Array parities are created during write operation, so performance for write operation is not as high as
RAID0.
• A read/write operation during data rebuilding will result in lower performance.