EM78P221/2N
8-Bit Microcontroller with OTP ROM
44 •
Product Specification (V1.0) 10.19.2007
(This specification is subject to change without further notice)
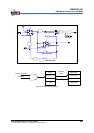
6.8.3 External RC Oscillator Mode
For some applications that do not require
precise timing calculation, the RC
oscillator (Fig. 6-14) could offer a
cost-effective oscillator configuration.
Nevertheless, it should be noted that the
frequency of the RC oscillator is
influenced by the supply voltage, the
values of the resistor (Rext), the capacitor
(Cext), and even by the operation
temperature. Moreover, the frequency
also changes slightly from one chip to
another due to manufacturing process
variations.
OSCI
Vcc
Rext
Cext
Fig. 6-14 External RC Oscillator Mode Circuit
In order to maintain a stable system frequency, the values of the Cext should not be
less than 20pF, and the value of Rext should not be greater than 1MΩ. If the frequency
cannot be kept within this range, the frequency can be easily affected by noise,
humidity, and leakage.
The smaller the Rext in the RC oscillator, the faster its frequency will be. On the
contrary, for very low Rext values, for instance, 1 KΩ, the oscillator will become
unstable because the NMOS cannot discharge the capacitance current correctly.
Based on the above reasons, it must be kept in mind that all the supply voltage, the
operation temperature, the components of the RC oscillator, the package types, and
the PCB is layout, have certain effect on the system frequency.
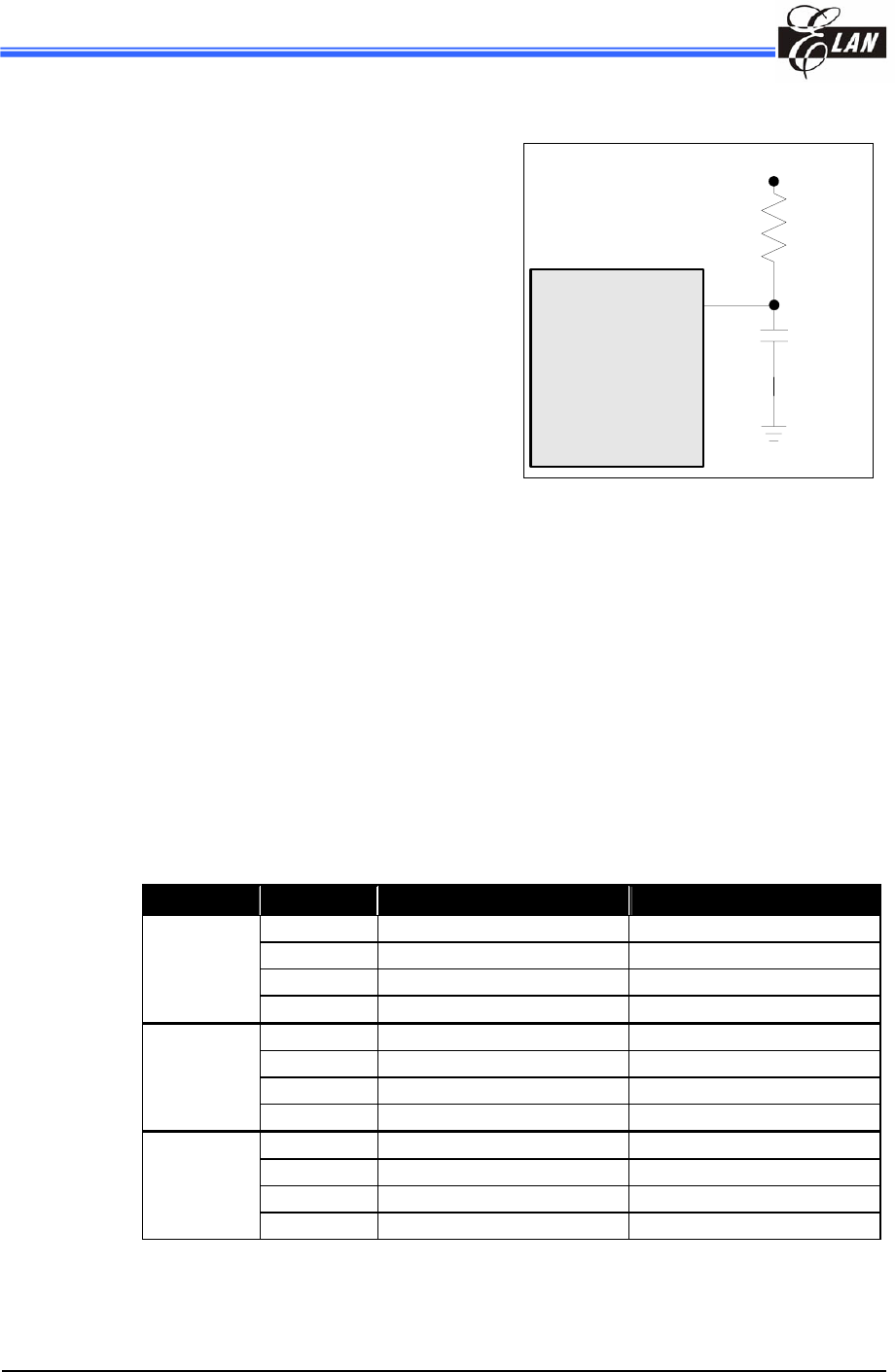
The RC Oscillator frequencies:
Cext Rext Average Fosc 5V, 25°C Average Fosc 3V, 25°C
3.3k 3.5 MHz 3.2 MHz
5.1k 2.5 MHz 2.3 MHz
10k 1.30 MHz 1.25 MHz
20 pF
100k 140 kHz 140 kHz
3.3k 1.27 MHz 1.21 MHz
5.1k 850 kHz 820 kHz
10k 450 kHz 450 kHz
100 pF
100k 48 kHz 50 kHz
3.3k 560 kHz 540 kHz
5.1k 370 kHz 360 kHz
10k 196 kHz 192 kHz
300 pF
100k 20 kHz 20 kHZ
Note:
1
: Measured based on DIP packages.
2
: The values are for design reference only.
3
: The frequency drift is ± 30%