Intel
®
6321ESB ICH—Thermal Solution Requirements
Intel
®
631xESB/632xESB I/O Controller Hub for Embedded Applications
TMDG February 2007
14
Example 1. Calculating the Required Thermal Performance
The cooling performance, Ψ
CA,
is defined using the thermal characterization parameter
previously described. The process to determine the required thermal performance to
cool the device includes:
1. Define a target component temperature T
CASE
and corresponding TDP.
2. Define a target local ambient temperature, T
LA
.
3. Use Equation 1 and Equation 2 to determine the required thermal performance
needed to cool the device.
The following provides an example of how you might determine the appropriate
performance targets.
Assume:
• TDP = 12.4 W and T
CASE
= 105° C
• Local processor ambient temperature, T
LA
= 65° C.
Then the following could be calculated using Equation 1 for the given chipset
configuration:
To determine the required heat sink performance, a heat sink solution provider would
need to determine Ψ
CS
performance for the selected TIM and mechanical load
configuration. If the heat sink solution were designed to work with a TIM material
performing at Ψ
CS
≤ 0.35 °C/W, solving from Equation 2, the performance needed from
the heat sink is:
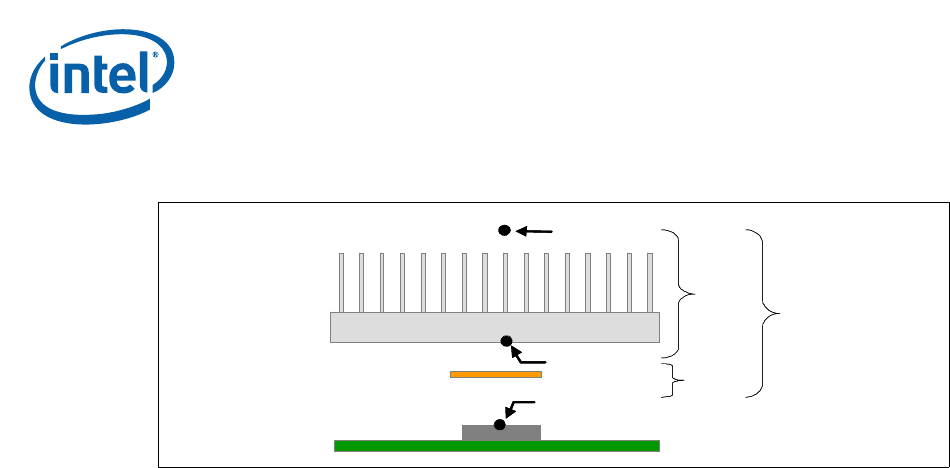
Figure 5. Processor Thermal Characterization Parameter Relationships
T
S
T
C
T
A
Ψ
SA
Ψ
CS
Ψ
CA
TIM
Device
T
S
T
C
T
A
Ψ
SA
Ψ
CS
Ψ
CA
HEATSINK
Ψ
CA
T
CASE
T
LA
–
TDP
-------------------------
105 65–
12.4
---------------
3.23°
C
W
----
===