USER GUIDE
46
Force - Tries to make an encrypted connection.
SSL Certificate Management
IP Extender uses the SSL (Secure Socket Layer) protocol for any encrypted network
traffic between itself and a connected client. When connecting, IP Extender reveals
its identity to a client using a cryptographic certificate. This is the same for all IP
Extenders and won't match the network configurations applied to the card by its
user. The certificate's underlying secret key is also used for securing the SSL
handshake. Hence, this is a security risk (but better than no encryption at all).
You can generate and install a new certificate unique to a particular card. IP
Extender can generate a new cryptographic key and the associated Certificate
Signing Request that needs to be certified by a certification authority (CA). A CA
verifies you are who you claim to be and signs and issues a SSL certificate to you.
To create and install a IP Extender SSL certificate:
1. From the Security Settings page choose Create your own SSL certificate. The
window appears as in Figure 31.
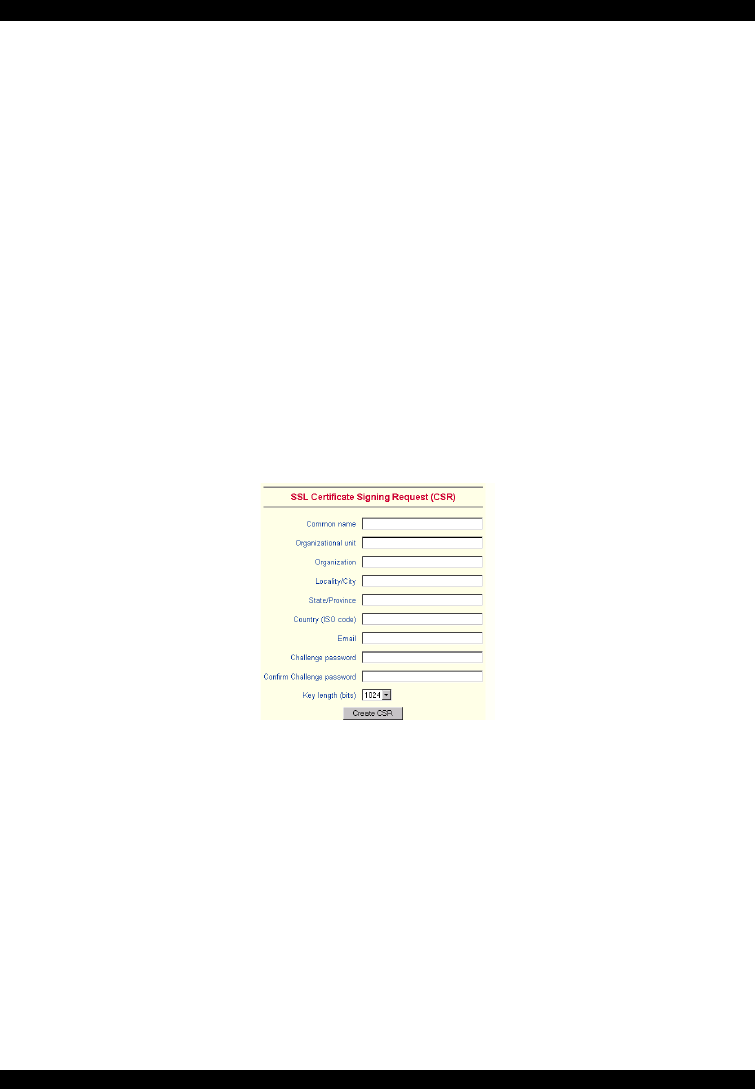
Figure 31 CSR
2. Fill in the fields:
Common name - Network name of IP Extender once installed in the user's network.
It is identical to the name that is used to access the card with a Web browser. In case
the name given here and the actual network name differ, the browser will pop up a
security warning when the card is accessed over HTTPS.
Organizational unit - Specifies which department within an organization IP
Extender belongs.
Organization/Locality/City/State/Province - Organization to which IP Extender
belongs + location.
Country - Use the 2 letter ISO code, e.g. DE for Germany.


















