Chapter 2 Hardware Overview of the NI 783xR
NI 783xR User Manual 2-14 ni.com
Common-Mode Signal Rejection Considerations
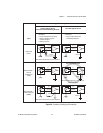
Figure 2-5 and Figure 2-8 show connections for signal sources that are
already referenced to some ground point with respect to the NI 783xR.
In these cases, the instrumentation amplifier can reject any voltage caused
by ground potential differences between the signal source and the device.
With differential input connections, the instrumentation amplifier can
reject common-mode noise pickup in the leads connecting the signal
sources to the device. The instrumentation amplifier can reject
common-mode signals when V+
in
and V–
in
(input signals) are both within
their specified input ranges. Refer to Appendix A, Specifications, for more
information about input ranges.
Analog Output
The bipolar output range of the NI 783xR AO channels is fixed at ±10 V.
Some applications require that the AO channels power on to known voltage
levels. To set the power-on levels, you can configure the NI 783xR to load
and run a VI when the system powers on. The VI can set the AO channels
to the desired voltage levels. The VI interprets data written to the DAC in
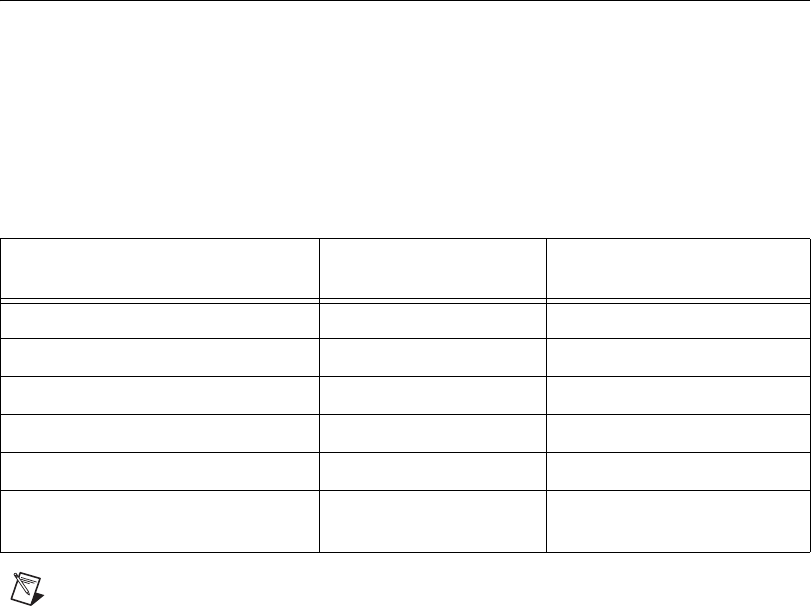
two’s complement format. Table 2-3 shows the ideal AO voltage generated
for a given input code.
Note If your VI does not set the output value for an AO channel, then the AO channel
voltage output will be undefined.
Table 2-3. Ideal Output Voltage and Input Code Mapping
Output Description AO Voltage
Input Code (Hex)
(Two’s Complement)
Full-scale range –1 LSB 9.999695 7FFF
Full-scale range –2 LSB 9.999390 7FFE
Midscale 0.000000 0000
Negative full-scale range, +1 LSB –9.999695 8001
Negative full-scale range –10.000000 8000
Any output voltage —
AO Voltage
10.0 V
-------------------------------
32,768×