SUPERSTAR II User Manual Rev 3 67
Appendix G GPS Overview
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite navigation system capable of providing a highly accurate,
continuous global navigation service independent of other positioning aids. GPS provides 24-hour, all-weather,
worldwide coverage with position, velocity and timing information.
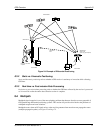
The system uses the NAVSTAR (NAVigation Satellite Timing And Ranging) satellites which consists of 24
operational satellites to provide a GPS receiver with at least six satellites in view at all times. A minimum of
four satellites in view are needed to allow the receiver to compute its current latitude, longitude, altitude with
reference to mean sea level and the GPS system time.
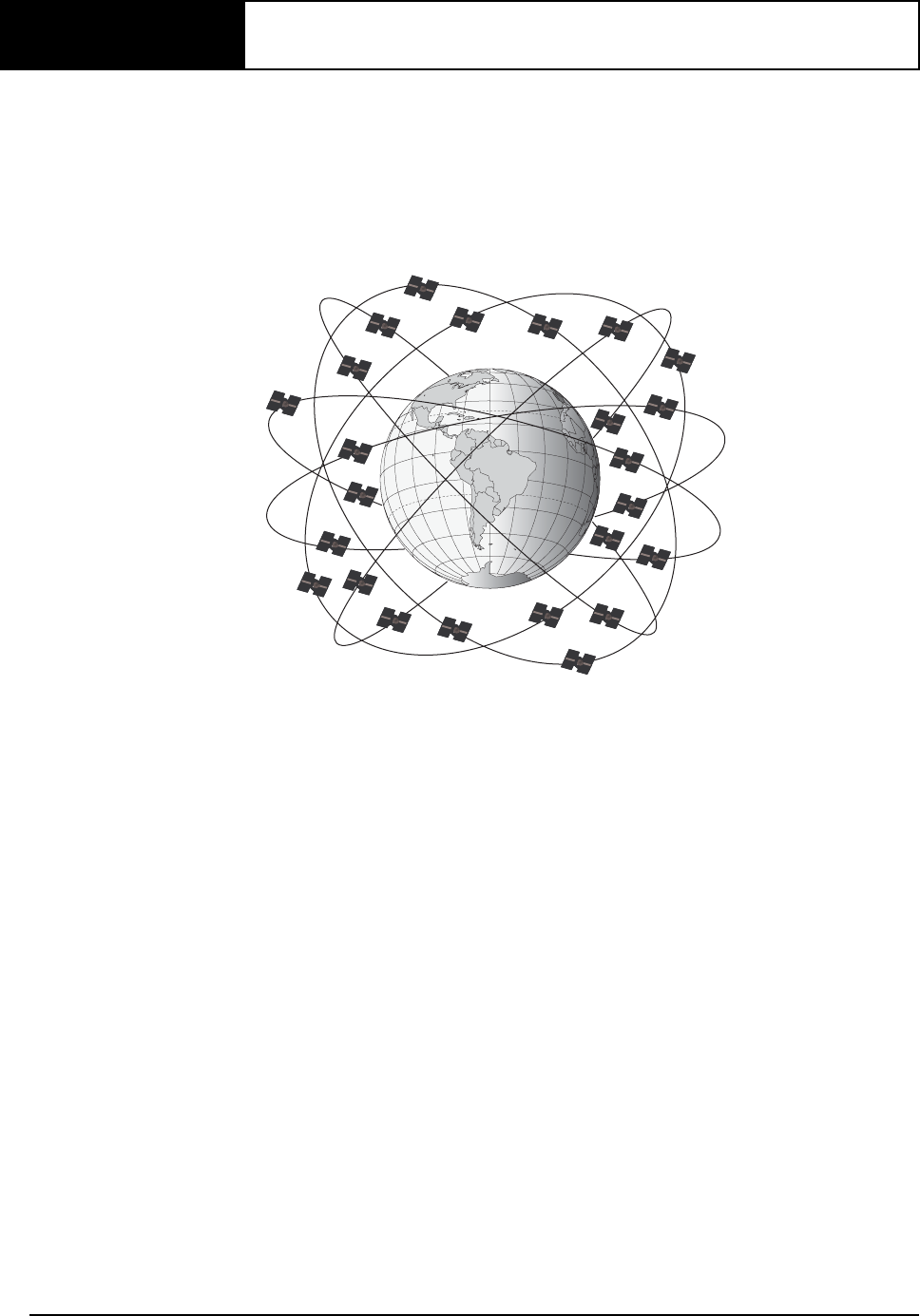
Figure 21: NAVSTAR Satellite Orbit Arrangement
G.1 GPS System Design
The GPS system design consists of three parts:
• The Space segment
• The Control segment
• The User segment
All these parts operate together to provide accurate three dimensional positioning, timing and velocity data to
users worldwide.
G.1.1 The Space Segment
The space segment is composed of the NAVSTAR GPS satellites. The constellation of the system consists of
24 satellites in six 55° orbital planes, with four satellites in each plane. The orbit period of each satellite is
approximately 12 hours at an altitude of 20 183 kilometers. This provides a GPS receiver with at least six
satellites in view from any point on earth, at any particular time.
The GPS satellite signal identifies the satellite and provides the positioning, timing, ranging data, satellite
status and the corrected ephemerides (orbit parameters) of the satellite to the users. The satellites can be
identified either by the Space Vehicle Number (SVN) or the Pseudorandom Code Number (PRN). The PRN is
used by the NovAtel receiver.
The GPS satellites transmit on two L-band frequencies; one centered at 1575.42 MHz (L1) and the other at
1227.60 MHz (L2). The L1 carrier is modulated by the C/A code (Coarse/Acquisition) and the P code