74 SUPERSTAR II User Manual Rev 3
Appendix G GPS Overview
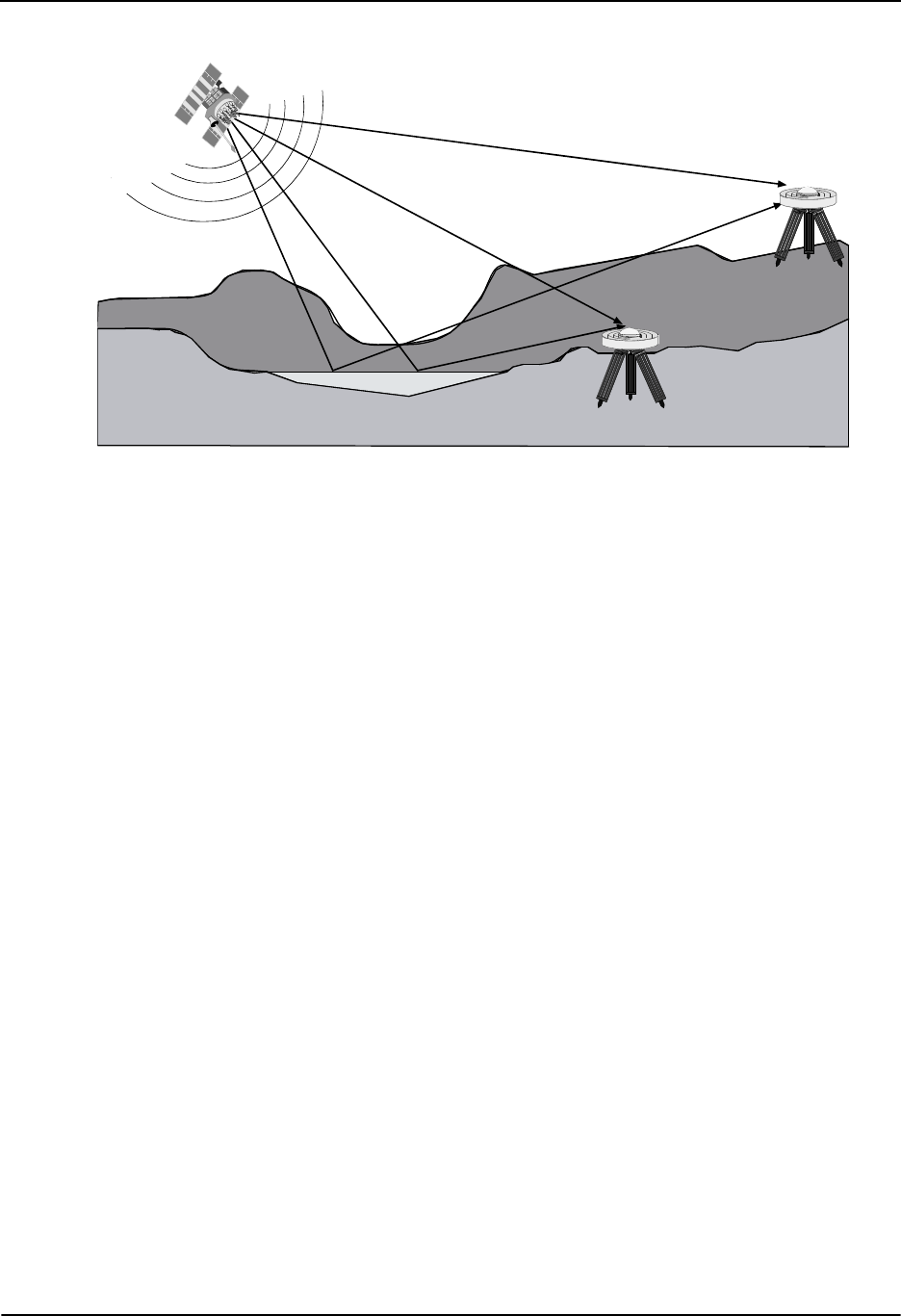
Figure 26: GPS Signal Multipath vs. Increased Antenna Height
When the antenna is in an environment with obstructions and reflective surfaces in the vicinity, it is
advantageous to mount the antenna as high as possible to reduce the obstructions, as well as reception from
reflective surfaces, as much as possible. See Figure 26 above for an example.
Water bodies are extremely good reflectors of GPS signals. Because of the short wavelengths at GPS
frequencies, even small ponds and water puddles can be a strong source of multipath reception, especially for
low angle satellites. Thus, it can be concluded that water bodies such as lakes and oceans are among the most
troublesome multipath environments for low angle signal reception. Obviously, water body reflections are a
constant problem for ocean going vessels.
G.4.3.2 Antenna Designs
Low angle reflections, such as from water bodies, can be reduced by careful selection of the antenna design.
For example, flat plate microstrip patch antennas have relatively poor reception properties at low elevation
angles near their radiation pattern horizon.
Quadrifilar helix antennas and other similar vertically high profile antennas tend to have high radiation gain
patterns at the horizon. These antennas, in general, are more susceptible to the problems resulting from low
angle multipath reception. So, for marine vessels, this type of antenna encourages multipath reception.
However, the advantages of good low angle reception also means that satellites can be acquired more easily
while rising in the horizon. As well, vessels subject to pitch and roll conditions will experience fewer
occurrences of satellite loss of lock.
Examples of the above antennas may be seen in Figure 27 on Page 75.
A good antenna design will also incorporate some form of left hand circular polarization (LHCP) rejection.
Multipath signals change polarization during the refraction and reflection process. This means that generally,
multipath signals may be LHCP oriented. This property can be used to advantage by GPS antenna designers. If
a GPS antenna is well designed for RHCP polarization, then LHCP multipath signals will automatically be
attenuated somewhat during the induction into the antenna. To further enhance performance, antennas can be
designed to increase the rejection of LHCP signals.