68 SUPERSTAR II User Manual Rev 3
Appendix G GPS Overview
(Precision) which is encrypted for military and other authorized users. The L2 carrier is modulated only with
the P code.
G.1.2 The Control Segment
The control segment consists of a master control station, five base stations and three data up-loading stations in
locations all around the globe.
The base stations track and monitor the satellites via their broadcast signals. The broadcast signals contain the
ephemeris data of the satellites, the ranging signals, the clock data and the almanac data. These signals are
passed to the master control station where the ephemerides are re-computed. The resulting ephemerides
corrections and timing corrections are transmitted back to the satellites through the data up-loading stations.
G.1.3 The User Segment
The user segment, such as the NovAtel receiver, consists of equipment which tracks and receives the satellite
signals. The user equipment must be capable of simultaneously processing the signals from a minimum of four
satellites to obtain accurate position, velocity and timing measurements.
G.2 Height Relationships
What is a geoid?
An equipotential surface is any surface where gravity is constant. This surface best represents mean sea-level
and not only covers the water but is projected throughout the continents. In North America this surface is most
commonly used at its zero value, i.e. all heights are referenced to this surface.
What is an ellipsoid?
An ellipsoid, also known as a spheroid, is a mathematical surface which is sometimes used to represent the
earth. Whenever you see latitudes and longitudes describing the location, this coordinate is being referenced to
a specific ellipsoid. GPS positions are referred to an ellipsoid known as WGS84 (World Geodetic System of
1984).
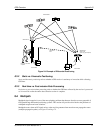
What is the relationship between a geoid and an ellipsoid?
The relationship between a geoid and an ellipsoid is shown in “Illustration of Receiver Height Measurements”
on Page 69.