Introduction
1-3
3160-A2-GB21-80
March 1999
SNMP Management Support
SNMP is a network management protocol that is used to monitor network
performance and status, and to report alarms (i.e., traps). To function, SNMP
requires a manager consisting of a software program housed within a workstation
or PC; an agent consisting of a software program housed within a device (e.g.,
the DSU/CSU); and a Management Information Base (MIB) consisting of a
database of managed objects. The DSU/CSU can be managed by any
industry-standard SNMP manager.
Two link layer protocols, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and Serial Line Internet
Protocol (SLIP), are supported for connection to an external SNMP manager or
network device (e.g., a router).
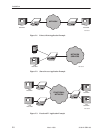
The SNMP manager or network device can be directly connected to the
communications (COM) port. An external LAN Adapter can be connected to
either the COM port or the auxiliary (AUX) port to provide Ethernet connectivity.
Also, the DSU/CSU can be daisy chained together by connecting the COM port of
one device to the AUX port of the other, providing SNMP connectivity.
The SNMP management system can communicate to the DSU/CSU remotely
through the Facility Data Link (FDL) or (for 2-port and 4-port DSU/CSUs) the
synchronous data port’s Embedded Data Link (EDL).
Physical Description
The 316x Series consists of a Model 3160 DSU/CSU (2-port), a Model 3164
DSU/DSU (4-port), a Model 3165 DSU/CSU (1-port), and a Model 3161
(carrier-mounted) DSU/CSU.
For more information about the carrier-mounted DSU/CSU, refer to the
ACCULINK 3151 CSU and 3161 DSU/CSU General Information Guide
and the
COMSPHERE 3000 Series Carrier Installation Manual
.
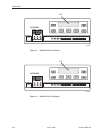
Standalone DSU/CSU Front Panel
The standalone DSU/CSU front panel contains,
H One 2-line, 16-alphanumeric-character-per-line liquid crystal display (LCD)
H One 7-button keypad (three Function and four directional keys)
H Twelve light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
H Six test jacks for the Model 3160/3164 DSU/CSU, and two test jacks for the
Model 3165 DSU/CSU
The front panels are shown in Figures 1-1, 1-2, and 1-3.