Introduction 88
Models 2603, 2621, and 2635 Getting Started Guide 8 • DHCP and DNS Configuration
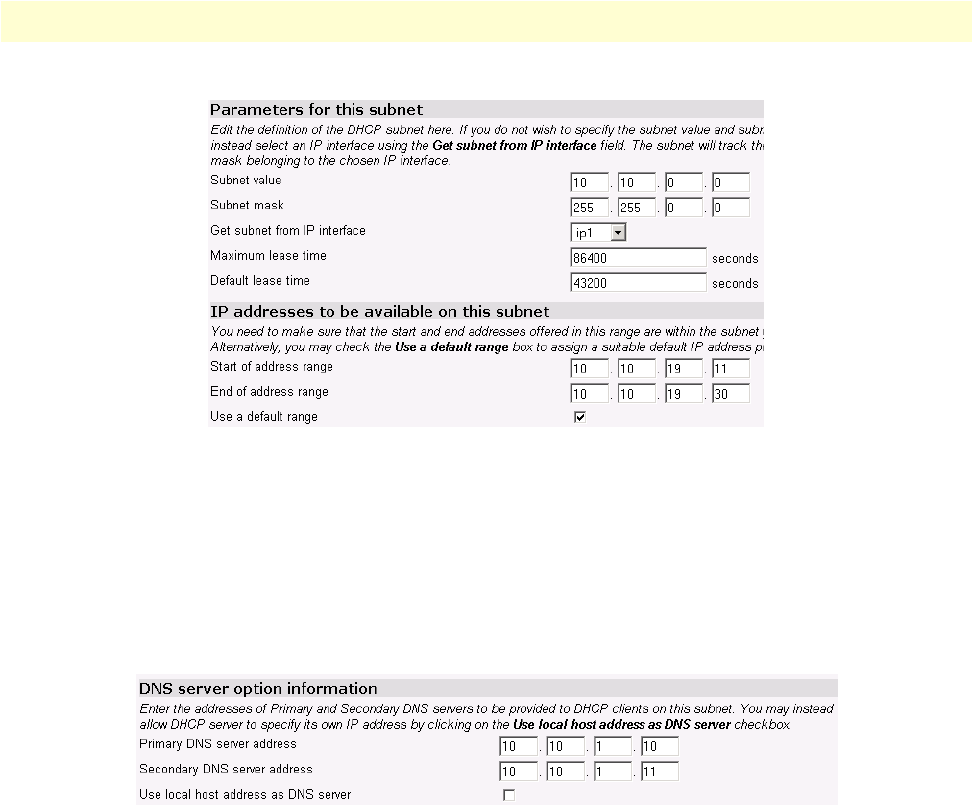
Figure 59. Example based on default range of IP address pool
DNS server option information
When a client requests an IP address from a DHCP server, the server can also send the IP addresses of the pri-
mary and secondary DNS servers’ IP addresses. The IPLink can accomplish this in one of two ways, neither
really having an advantage over the other. This section of the configuration page is one method, the other is
DNS Relay to be described later in this chapter. Refer to figure 60.
Figure 60. Configuration of the DNS server IP addresses
Enter the IP addresses of the primary and secondary DNS servers. Subsequently, the client will receive these
addresses when assigned an IP address. When the client makes a DNS inquiry, it sends the request directly to
the appropriate DNS server. The IPLink router merely forwards the packet.
The third parameter is ‘Use local host address as DNS server’ which is the IP address of the IPLink. In this sce-
nario, the client considers the IPLink as a DNS server by sending all requests to the IPLink’s IP address. The
IPLink forwards the request to the DNS servers using the IP address of the actual servers. You still need to
define the IP addresses of the primary and secondary DNS servers in the section because the IPLink needs to
know in order to forward the DNS requests.


















