43
2#* 0&
2& :
The Switch is implemented with an address table. This address table composed of many entries. Each entry is
used to store the address information of some node in network, including MAC address, port no, etc. This
information comes from the learning process of Ethernet Switch.
2'
When one packet comes in from any port, the Switch will record the source address, port no. And the other
related information in address table. This information will be used to decide either forwarding or filtering for
future packets.
2! ;!
When one packet comes from some port of the Ethernet Switching, it will also check the destination address
besides the source address learning. The Ethernet Switching will lookup the address-table for the destination
address. If not found, this packet will be forwarded to all the other ports except the port, which this packet
comes in. And these ports will transmit this packet to the network it connected. If found, and the destination
address is located at different port from this packet comes in, the Ethernet Switching will forward this packet to
the port where this destination address is located according to the information from address table. But, if the
destination address is located at the same port with this packet comes in, then this packet will be filtered.
Thereby increasing the network throughput and availability
2"#+ +!
Store-and-Forward is one type of packet-forwarding techniques. A Store-and-Forward Ethernet Switching
stores the incoming frame in an internal buffer, do the complete error checking before transmission. Therefore,
no error packets occurrence, it is the best choice when a network needs efficiency and stability.
The Ethernet Switch scans the destination address from the packet-header, searches the routing table
provided for the incoming port and forwards the packet, only if required. The fast forwarding makes the switch
attractive for connecting servers directly to the network, thereby increasing throughput and availability.
However, the switch is most commonly used to segment existence hubs, which nearly always improves overall
performance. An Ethernet Switching can be easily configured in any Ethernet network environment to
significantly boost bandwidth using conventional cabling and adapters.
Due to the learning function of the Ethernet switching, the source address and corresponding port number of
each incoming and outgoing packet are stored in a routing table. This information is subsequently used to filter
packets whose destination address is on the same segment as the source address. This confines network
traffic to its respective domain, reducing the overall load on the network.
The Switch performs "Store and forward" therefore, no error packets occur. More reliably, it reduces the
re-transmission rate. No packet loss will occur.
22&+
The STP ports on the Switch have built-in “Auto-negotiation”. This technology automatically sets the best
possible bandwidth when a connection is established with another network device (usually at Power On or
Reset). This is done by detect the modes and speeds at the second of both device is connected and capable of,
Both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX devices can connect with the port in either Half- or Full-Duplex mode.
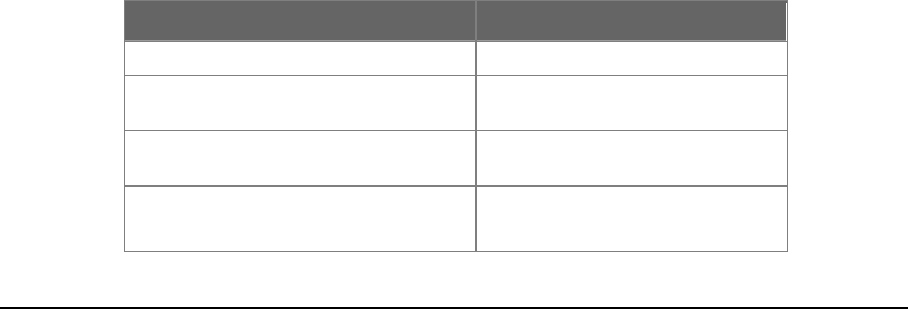
If attached device is: 100Base-TX port will set to:
• 10Mbps, no auto-negotiation
10Mbps
• 10Mbps, with auto-negotiation
10/20Mbps (10Base-T/Full-Duplex)
• 100Mbps, no auto-negotiation
100Mbps
• 100Mbps, with auto-negotiation
100/200Mbps
(100Base-TX/Full-Duplex)


















