User’s Manual of SGSD-1022 / SGSD-1022P
SGSW-2840 / SGSW-2840P
218
4.9.3 Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR)
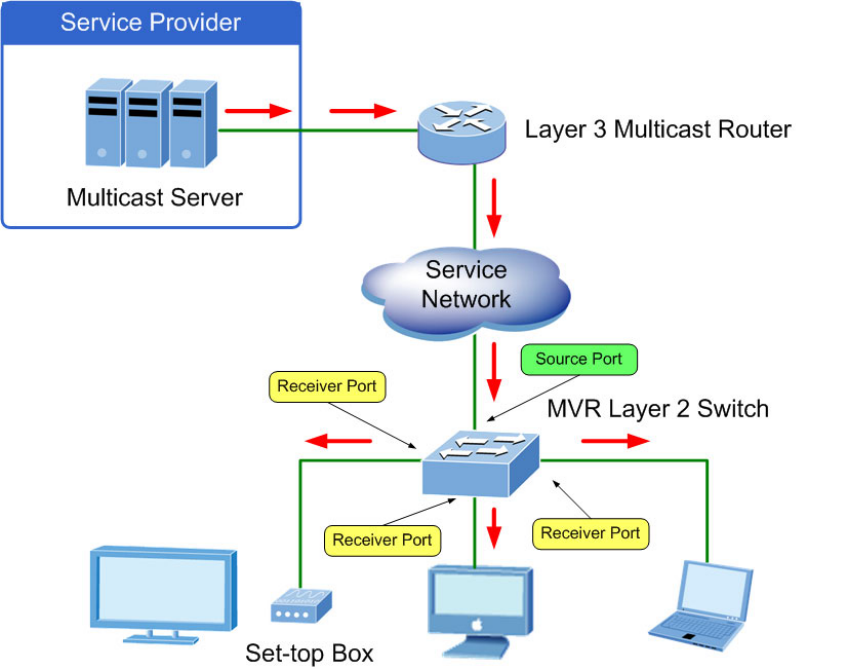
Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) is a protocol that controls access to a single network-wide VLAN most commonly used for
transmitting multicast traffic (such as television channels or video-on-demand) across a service provider’s network. Any
multicast traffic entering an MVR VLAN is sent to all attached subscribers. This protocol can significantly reduce the processing
overhead required to dynamically monitor and establish the distribution tree for a normal multicast VLAN. This makes it possible
to support common multicast services over a wide part of the network without having to use any multicast routing protocol.
MVR maintains the user isolation and data security provided by VLAN segregation by passing only multicast traffic into other
VLANs to which the subscribers belong. Even though common multicast streams are passed onto different VLAN groups from
the MVR VLAN, users in different IEEE 802.1Q or private VLANs cannot exchange any information (except through upper-level
routing services).
General Configuration Guidelines for MVR
1. Enable MVR globally on the Managed Switch, select the MVR VLAN, and add the multicast groups that will stream traffic
to attached hosts (see “Configuring Global MVR Settings”).
2. Set the interfaces that will join the MVR as source ports or receiver ports (see “Configuring MVR Interface Status”).
3. Enable IGMP Snooping to an allow a subscriber to dynamically join or leave an MVR group (see “Configuring IGMP
Snooping and Query Parameters”).


















