Spinpoint M8U-Internal Product Manual REV 3.4
33
INSTALLATION
6.2.1 Mechanical Interface
This chapter provides the mechanical and electrical specifications for the cables, connectors, and cable
assemblies used to interconnect USB devices. The specification includes the dimensions, materials,
electrical, and reliability requirements. This chapter documents minimum requirements for the external
USB interconnect. Substitute material may be used as long as it meets these minimums.
6.2.1.1 Mechanical Overview
All devices have an upstream connection. Upstream and downstream connectors are not mechanically
interchangeable, thus eliminating illegal loopback connections at hubs. The cable has four conductors: a
twisted signal pair of standard gauge and a power pair in a range of permitted gauges. The connector is four-
position, with shielded housing, specified robustness, and ease of attach-detach characteristics.
The USB physical topology consists of connecting the downstream hub port to the upstream port of another
hub or to a device. The USB can operate at three speeds. High-speed (480 Mb/s) and full-speed (12 Mb/s)
require the use of a shielded cable with two power conductors and twisted pair signal conductors. Lowspeed
(1.5 Mb/s) recommends, but does not require the use of a cable with twisted pair signal conductors.
The connectors are designed to be hot plugged.
6.2.1.2 Connector
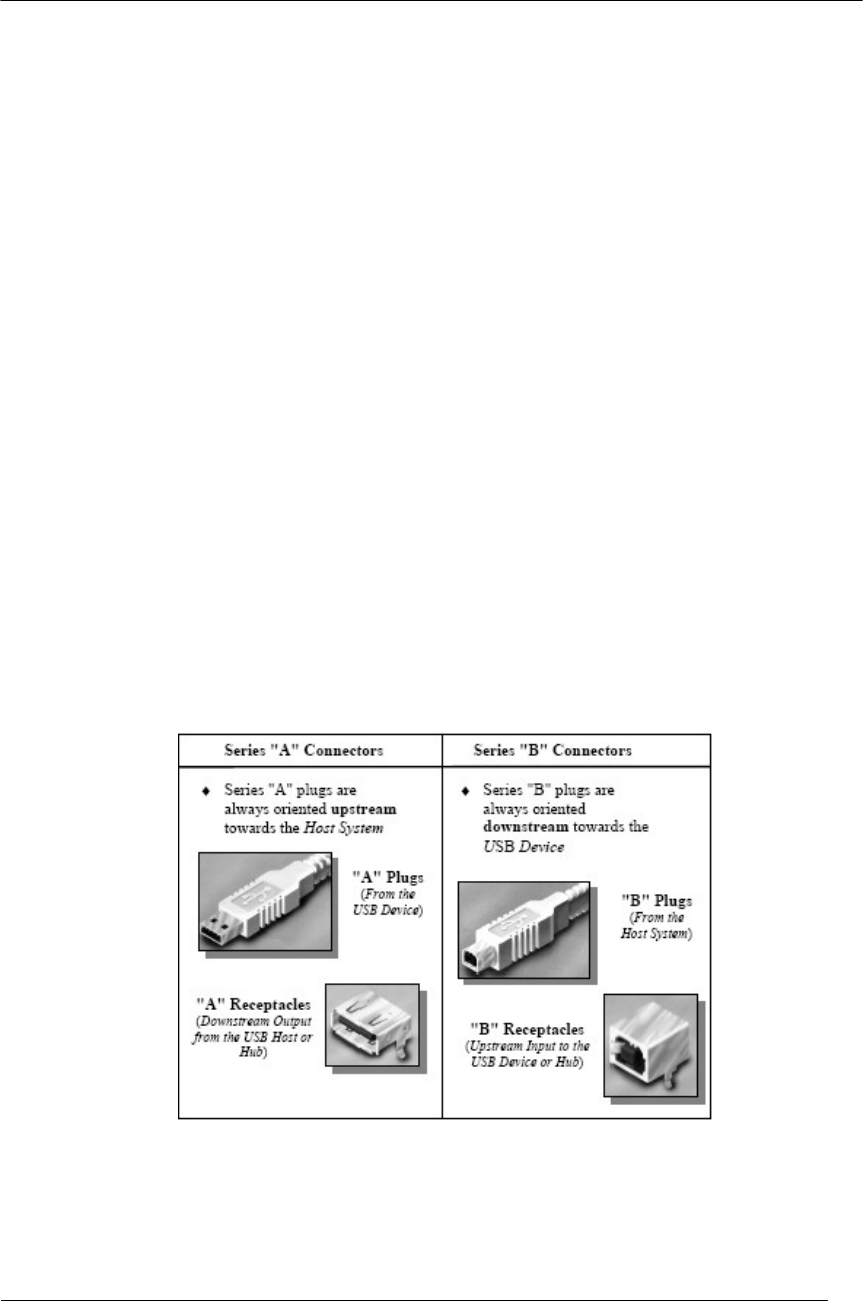
To minimize end user termination problems, USB uses a “keyed connector” protocol. The physical
difference in the Series “A” and “B” connectors insures proper end user connectivity. The “A” connector
is the principle means of connecting USB devices directly to a host or to the downstream port of a hub. All
USB devices must have the standard Series “A” connector specified in this chapter. The “B” connector
allows device vendors to provide a standard detachable cable. This facilitates end user cable replacement.
Figure 6-2 illustrates the keyed connector protocol.
Figure 6-2: Keyed Connector Protocol
The following list explains how the plugs and receptacles can be mated:
Series “A” receptacle mates with a Series “A” plug. Electrically, Series “A” receptacles function as
outputs from host systems and/or hubs.
Series “A” plug mates with a Series “A” receptacle. The Series “A” plug always is oriented towards